Home > Press > Rice U. chemists create 3-D printed graphene foam
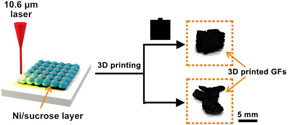 |
| 3-D graphene foam objects are produced by shining a laser on a mixture of powdered sugar and nickel powder. The laser is moved back and forth to melt sugar in a 2-D pattern, and nickel acts as a catalyst to spur the growth of graphene foam. The process is repeated with successive layers of powder to build up 3-D objects. (Image courtesy of Tour Group/Rice University) |
Abstract:
Nanotechnologists from Rice University and China's Tianjin University have used 3-D laser printing to fabricate centimeter-sized objects of atomically thin graphene.
Rice U. chemists create 3-D printed graphene foam
Houston, TX | Posted on June 22nd, 2017The research could yield industrially useful quantities of bulk graphene and is described online in a new study in the American Chemical Society journal ACS Nano.
"This study is a first of its kind," said Rice chemist James Tour, co-corresponding author of the paper. "We have shown how to make 3-D graphene foams from nongraphene starting materials, and the method lends itself to being scaled to graphene foams for additive manufacturing applications with pore-size control."
Graphene, one of the most intensely studied nanomaterials of the decade, is a two-dimensional sheet of pure carbon that is both ultrastrong and conductive. Scientists hope to use graphene for everything from nanoelectronics and aircraft de-icers to batteries and bone implants. But most industrial applications would require bulk quantities of graphene in a three-dimensional form, and scientists have struggled to find simple ways of creating bulk 3-D graphene.
For example, researchers in Tour's lab began using lasers, powdered sugar and nickel to make 3-D graphene foam in late 2016. Earlier this year they showed that they could reinforce the foam with carbon nanotubes, which produced a material they dubbed "rebar graphene" that could retain its shape while supporting 3,000 times its own weight. But making rebar graphene was no simple task. It required a pre-fabricated 3-D mold, a 1,000-degree Celsius chemical vapor deposition (CVD) process and nearly three hours of heating and cooling.
In the latest study, a team from Tour's lab and the labs of Rice's Jun Luo and Tianjin's Naiqin Zhao adapted a common 3-D printing technique to make fingertip-size blocks of graphene foam. The process is conducted at room temperature. No molds are required and the starting materials are powdered sugar and nickel powder.
"This simple and efficient method does away with the need for both cold-press molds and high-temperature CVD treatment," said co-lead author Junwei Sha, a former student in Tour's lab who is now a postdoctoral researcher at Tianjin. "We should also be able to use this process to produce specific types of graphene foam like 3-D printed rebar graphene as well as both nitrogen- and sulfur-doped graphene foam by changing the precursor powders."
Three-D laser printers work differently than the more familiar extrusion-based 3-D printers, which create objects by squeezing melted plastic through a needle as they trace out two-dimensional patterns. In 3-D laser sintering, a laser shines down onto a flat bed of powder. Wherever the laser touches powder, it melts or sinters the powder into a solid form. The laser is rastered, or moved back and forth, line by line to create a single two-dimensional slice of a larger object. Then a new layer of powder is laid over the top of that layer and the process is repeated to build up three-dimensional objects from successive two-dimensional layers.
The new Rice process used a commercially available CO2 laser. When this laser was shone onto the sugar and nickel powder, the sugar was melted and the nickel acted as a catalyst. Graphene formed as the mixture cooled after the laser had moved on to melt sugar in the next spot, and Sha and colleagues conducted an exhaustive study to find the optimal amount of time and laser power to maximize graphene production.
The foam created by the process is a low-density, 3-D form of graphene with large pores that account for more than 99 percent of its volume.
"The 3-D graphene foams prepared by our method show promise for applications that require rapid prototyping and manufacturing of 3-D carbon materials, including energy storage, damping and sound absorption," said co-lead author Yilun Li, a graduate student at Rice.
Tour is the T.T. and W.F. Chao Chair in Chemistry as well as a professor of computer science and of materials science and nanoengineering at Rice.
Additional co-authors include Rodrigo Villegas Salvatierra, Tuo Wang, Pei Dong, Yongsung Ji, Seoung-Ki Lee, Chenhao Zhang, Jibo Zhang and Pulickel Ajayan, all of Rice, and Robert Smith of Qualified Rapid Products in West Jordan, Utah.
The research was supported by the Air Force Office of Scientific Research and its Multidisciplinary University Research Initiative, the China Scholarship Council, the State Key Program of National Natural Science of China, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Special Foundation for Science and Technology Major Program of Tianjin and Universal Laser Systems.
####
About Rice University
Located on a 300-acre forested campus in Houston, Rice University is consistently ranked among the nation’s top 20 universities by U.S. News & World Report. Rice has highly respected schools of Architecture, Business, Continuing Studies, Engineering, Humanities, Music, Natural Sciences and Social Sciences and is home to the Baker Institute for Public Policy. With 3,879 undergraduates and 2,861 graduate students, Rice’s undergraduate student-to-faculty ratio is 6-to-1. Its residential college system builds close-knit communities and lifelong friendships, just one reason why Rice is ranked No. 1 for happiest students and for lots of race/class interaction by the Princeton Review. Rice is also rated as a best value among private universities by Kiplinger’s Personal Finance. To read “What they’re saying about Rice,” go to http://tinyurl.com/RiceUniversityoverview .
Follow Rice News and Media Relations on Twitter @RiceUNews.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Jade Boyd
713-348-6778
Copyright © Rice University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() A copy of the paper is available at:
A copy of the paper is available at:
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
2 Dimensional Materials
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Closing the gaps — MXene-coating filters can enhance performance and reusability February 28th, 2025
Closing the gaps — MXene-coating filters can enhance performance and reusability February 28th, 2025
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
3D & 4D printing/Additive-manufacturing
![]() Presenting: Ultrasound-based printing of 3D materials—potentially inside the body December 8th, 2023
Presenting: Ultrasound-based printing of 3D materials—potentially inside the body December 8th, 2023
![]() Fiber sensing scientists invent 3D printed fiber microprobe for measuring in vivo biomechanical properties of tissue and even single cell February 10th, 2023
Fiber sensing scientists invent 3D printed fiber microprobe for measuring in vivo biomechanical properties of tissue and even single cell February 10th, 2023
![]() 3D-printed decoder, AI-enabled image compression could enable higher-res displays December 9th, 2022
3D-printed decoder, AI-enabled image compression could enable higher-res displays December 9th, 2022
![]() Researchers design new inks for 3D-printable wearable bioelectronics: Potential uses include printing electronic tattoos for medical tracking applications August 19th, 2022
Researchers design new inks for 3D-printable wearable bioelectronics: Potential uses include printing electronic tattoos for medical tracking applications August 19th, 2022
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
Industrial
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() Quantum interference in molecule-surface collisions February 28th, 2025
Quantum interference in molecule-surface collisions February 28th, 2025
![]() Boron nitride nanotube fibers get real: Rice lab creates first heat-tolerant, stable fibers from wet-spinning process June 24th, 2022
Boron nitride nanotube fibers get real: Rice lab creates first heat-tolerant, stable fibers from wet-spinning process June 24th, 2022
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








