Home > Press > Graphene and quantum dots put in motion a CMOS-integrated camera that can see the invisible
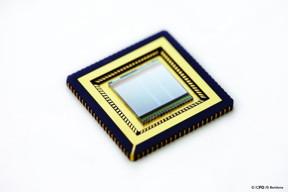 |
| Graphene-quantum dots-CMOS-based sensor for ultraviolet, visible and infrared. CREDIT ICFO/ D. Bartolome |
Abstract:
Over the past 40 years, microelectronics have advanced by leaps and bounds thanks to silicon and CMOS (Complementary metal-oxide semiconductors) technology, making possible computing, smartphones, compact and low-cost digital cameras, as well as most of the electronic gadgets we rely on today.
ICFO researchers have developed the first graphene -- quantum dots -- CMOS integrated based camera, capable of imaging visible and infrared light at the same time. The camera will be useful for many applications that include night vision, food inspection, fire control, vision under extreme weather conditions, to name a few. The imaging system is based on the first monolithic integration of graphene and quantum dot photodetectors with a CMOS read-out integrated circuit. It has proven to be easy and cheap to fabricate at room temperature and under ambient conditions, allowing for low-cost mass-production.
Credit: ICFO-The Institute of Photonic Sciences
Graphene and quantum dots put in motion a CMOS-integrated camera that can see the invisible
Barcelona, Spain | Posted on May 29th, 2017However, the diversification of this platform into applications other than microcircuits and visible light cameras has been impeded by the difficulty to combine semiconductors other than silicon with CMOS.
This obstacle has now been overcome. ICFO researchers have shown for the first time the monolithic integration of a CMOS integrated circuit with graphene, resulting in a high-resolution image sensor consisting of hundreds of thousands of photodetectors based on graphene and quantum dots (QD). They operated it as a digital camera that is highly sensitive to UV, visible and infrared light at the same time. This has never been achieved before with existing imaging sensors. In general, this demonstration of monolithic integration of graphene with CMOS enables a wide range of optoelectronic applications, such as low-power optical data communications and compact and ultra sensitive sensing systems.
The study was published in Nature Photonics, and highlighted on the front cover image. The work was carried out by ICFO researchers Stijn Goossens, Gabriele Navickaite, Carles Monasterio, Schuchi Gupta, Juan Jose Piqueras, Raul Perez, Gregory Burwell, Ivan Nitkitsky, Tania Lasanta, Teresa Galan, Eric Puma, and led by ICREA Professors Frank Koppens and Gerasimos Konstantatos, in collaboration with the company Graphenea. The graphene-QD image sensor was fabricated by taking PbS colloidal quantum dots, depositing them onto the CVD graphene and subsequently depositing this hybrid system onto a CMOS wafer with image sensor dies and a read-out circuit. As Stijn Goossens comments, "No complex material processing or growth processes were required to achieve this graphene-quantum dot CMOS image sensor. It proved easy and cheap to fabricate at room temperature and under ambient conditions, which signifies a considerable decrease in production costs. Even more, because of its properties, it can be easily integrated on flexible substrates as well as CMOS-type integrated circuits."
As ICREA Prof. at ICFO Gerasimos Konstantatos, expert in quantum dot-graphene research comments, "we engineered the QDs to extend to the short infrared range of the spectrum (1100-1900nm), to a point where we were able to demonstrate and detect the night glow of the atmosphere on a dark and clear sky enabling passive night vision. This work shows that this class of phototransistors may be the way to go for high sensitivity, low-cost, infrared image sensors operating at room temperature addressing the huge infrared market that is currently thirsty for cheap technologies".
"The development of this monolithic CMOS-based image sensor represents a milestone for low-cost, high-resolution broadband and hyperspectral imaging systems" ICREA Prof. at ICFO Frank Koppens highlights. He assures that "in general, graphene-CMOS technology will enable a vast amount of applications, that range from safety, security, low cost pocket and smartphone cameras, fire control systems, passive night vision and night surveillance cameras, automotive sensor systems, medical imaging applications, food and pharmaceutical inspection to environmental monitoring, to name a few".
This project is currently incubating in ICFO's Launchpad. The team is working with the institute's tech transfer professionals to bring this breakthrough along with its full patent portfolio of imaging and sensing technologies to the market.
###
This research has been partially supported by the European Graphene Flagship, European Research Council, the Government of Catalonia, Fundació Cellex and the Severo Ochoa Excellence program of the Government of Spain.
####
About ICFO-The Institute of Photonic Sciences
ICFO was created in 2002 by the government of Catalonia and the Technical University of Catalonia as a centre of research excellence devoted to the science and technologies of light with a triple mission: to conduct frontier research, train the next generation of scientists, and provide knowledge and technology transfer. Today, it is one of the top research centres worldwide in its category as measured by international rankings.
Research at ICFO targets the forefront of science and technology based on light with programs directed at applications in Health, Renewable Energies, Information Technologies, Security and Industrial processes, among others. The institute hosts 400 professionals based in a dedicated building situated in the Mediterranean Technology Park in the metropolitan area of Barcelona.
ICFO participates in a large number of projects and international networks of excellence and is host to the NEST program that is financed by Fundación Privada Cellex Barcelona. Ground-breaking research in graphene is being carried out at ICFO and through key collaborative research partnerships such as the FET Graphene Flagship. ICREA Professor at ICFO and NEST Fellow Frank Koppens is the leader of the Optoelectonics work package within the Flagship program.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Alina Hirschmann
34-935-542-246
Copyright © ICFO-The Institute of Photonic Sciences
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() Link to the research group led by ICREA Prof. Gerasimos Konstantatos:
Link to the research group led by ICREA Prof. Gerasimos Konstantatos:
![]() Link to the research group led by ICREA Prof. Frank Koppens:
Link to the research group led by ICREA Prof. Frank Koppens:
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
Videos/Movies
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Quantum Dots/Rods
![]() A new kind of magnetism November 17th, 2023
A new kind of magnetism November 17th, 2023
![]() IOP Publishing celebrates World Quantum Day with the announcement of a special quantum collection and the winners of two prestigious quantum awards April 14th, 2023
IOP Publishing celebrates World Quantum Day with the announcement of a special quantum collection and the winners of two prestigious quantum awards April 14th, 2023
![]() Qubits on strong stimulants: Researchers find ways to improve the storage time of quantum information in a spin rich material January 27th, 2023
Qubits on strong stimulants: Researchers find ways to improve the storage time of quantum information in a spin rich material January 27th, 2023
![]() NIST’s grid of quantum islands could reveal secrets for powerful technologies November 18th, 2022
NIST’s grid of quantum islands could reveal secrets for powerful technologies November 18th, 2022
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








