Home > Press > A new kind of magnetism
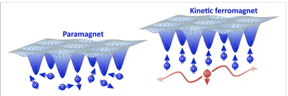 |
| In the moiré material produced at ETH, the electron spins are disordered if there is exactly one electron per lattice site (left). As soon as there are more electrons than lattice sites (right) and pairs of electrons can form doublons (red), the spins align ferromagnetically as this minimizes the kinetic energy. CREDIT ETH Zurich |
Abstract:
For a magnet to stick to a fridge door, inside of it several physical effects need to work together perfectly. The magnetic moments of its electrons all point in the same direction, even if no external magnetic field forces them to do so. This happens because of the so-called exchange interaction, a combination of electrostatic repulsion between electrons and quantum mechanical effects of the electron spins, which, in turn, are responsible for the magnetic moments. This is common explanation for the fact that certain materials like iron or nickel are ferromagnetic, or permanently magnetic, as long as one does not heat them above a particular temperature.
A new kind of magnetism
Zurich, Switzerland | Posted on November 17th, 2023At ETH in Zurich a team of researchers led by Ataç Imamoğlu at the Institute for Quantum Electronics and Eugene Demler at the Institute for Theoretical Physics have now detected a new type of ferromagnetism in an artificially produced material, in which the alignment of the magnetic moments comes about in a completely different way. They recently published their results in the scientific journal Nature.
Artificial material with electron filling
In Imamoğlu’s laboratory, PhD student Livio Ciorciaro, post-doc Tomasz Smolenski and colleagues produced a special material by putting atomically thin layers of two different semiconductor materials (molybdenum diselenide and tungsten disulfide) on top of each other. In the contact plane, the different lattice constants of the two materials – the separation between their atoms – leads to the formation of a two-dimensional periodic potential with a large lattice constant (thirty times larger than those of the two semiconductors), which can be filled with electrons by applying an electric voltage. “Such moiré materials have attracted great interest in recent years, as they can be used to investigate quantum effects of strongly interacting electrons very well”, says Imamoğlu. “However, so far very little was known about their magnetic properties.”
To investigate these magnetic properties, Imamoğlu and his coworkers measured whether for a certain electron filling the moiré material was paramagnetic, with its magnetic moments randomly oriented, or ferromagnetic. They illuminated the material with laser light and measured how strongly the light was reflected for different polarizations. The polarization indicates in which direction the electromagnetic field of the laser light oscillates, and depending on the orientation of the magnetic moments – and hence the electron spins – the material will reflect one polarization more strongly than the other. From this difference one can then calculate whether the spins point in the same direction or in different directions, from which the magnetization can be determined.
Striking evidence
By steadily increasing the voltage, the physicists filled the material with electrons and measured the corresponding magnetisation. Up to a filling of exactly one electron per site of the moiré lattice (also known as a Mott insulator), the material remained paramagnetic. As the researchers kept adding electrons to the lattice, something unexpected happened: the material suddenly behaved very much like a ferromagnet.
“That was striking evidence for a new type of magnetism that cannot be explained by the exchange interaction”, Imamoğlu says. In fact, if the exchange interaction were responsible for the magnetism, that should have shown up also with fewer electrons in the lattice. The sudden onset, therefore, pointed towards a different effect.
Kinetic magnetism
Eugene Demler, in collaboration with post-doc Ivan Morera, finally had the crucial idea: they could be looking at a mechanism which the Japanese physicist Yosuke Nagaoka had theoretically predicated as early as 1966. In that mechanism, by making their spins point in the same direction the electrons minimize their kinetic energy (energy of motion), which is much larger than the exchange energy. In the experiment performed by the ETH researchers, this happens as soon as there is more than one electron per lattice site inside the moiré material. As a consequence, pairs of electrons can team up to form so called doublons. The kinetic energy is minimized when the doublons can spread out over the entire lattice through quantum mechanical tunnelling. This, however, is only possible if the single electrons in the lattice align their spins ferromagnetically, as otherwise quantum mechanical superposition effects which enable the free expansion of the doublons are disturbed.
“Up to now, such mechanisms for kinetic magnetism have only been detected in model systems, for example in four coupled quantum dots”, says Imamoğlu, “but never in extended solid state systems like the one we use.”
As a next step, he wants to change the parameters of the moiré lattice in order to investigate whether the ferromagnetism is preserved for higher temperatures; in the current experiment that material still had to be cooled down to a tenth of a degree above absolute zero.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Media Contact
Peter Rueegg
ETH Zurich
Office: 446-324-532
Expert Contact
Atac Imamoglu
ETH Zurich
@ETH_en
Copyright © ETH Zurich
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Discoveries
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Quantum Dots/Rods
![]() IOP Publishing celebrates World Quantum Day with the announcement of a special quantum collection and the winners of two prestigious quantum awards April 14th, 2023
IOP Publishing celebrates World Quantum Day with the announcement of a special quantum collection and the winners of two prestigious quantum awards April 14th, 2023
![]() Qubits on strong stimulants: Researchers find ways to improve the storage time of quantum information in a spin rich material January 27th, 2023
Qubits on strong stimulants: Researchers find ways to improve the storage time of quantum information in a spin rich material January 27th, 2023
![]() NIST’s grid of quantum islands could reveal secrets for powerful technologies November 18th, 2022
NIST’s grid of quantum islands could reveal secrets for powerful technologies November 18th, 2022
![]() Lattice distortion of perovskite quantum dots induces coherent quantum beating September 9th, 2022
Lattice distortion of perovskite quantum dots induces coherent quantum beating September 9th, 2022
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








