Home > Press > Dual-function nanorod LEDs could make multifunctional displays
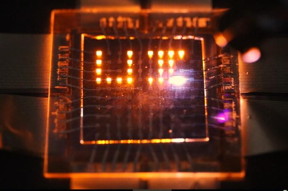 |
| A laser stylus writes on a small array of multifunction pixels made by dual-function LEDs than can both emit and respond to light. CREDIT Image courtesy of Moonsub Shim, University of Illinois |
Abstract:
Cellphones and other devices could soon be controlled with touchless gestures and charge themselves using ambient light, thanks to new LED arrays that can both emit and detect light.
Dual-function nanorod LEDs could make multifunctional displays
Champaign, IL | Posted on February 11th, 2017Made of tiny nanorods arrayed in a thin film, the LEDs could enable new interactive functions and multitasking devices. Researchers at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign and Dow Electronic Materials in Marlborough, Massachusetts, report the advance in the Feb. 10 issue of the journal Science.
"These LEDs are the beginning of enabling displays to do something completely different, moving well beyond just displaying information to be much more interactive devices," said Moonsub Shim, a professor of materials science and engineering at the U. of I. and the leader of the study. "That can become the basis for new and interesting designs for a lot of electronics."
The tiny nanorods, each measuring less than 5 nanometers in diameter, are made of three types of semiconductor material. One type emits and absorbs visible light. The other two semiconductors control how charge flows through the first material. The combination is what allows the LEDs to emit, sense and respond to light.
The nanorod LEDs are able to perform both functions by quickly switching back and forth from emitting to detecting. They switch so fast that, to the human eye, the display appears to stay on continuously -- in fact, it's three orders of magnitude faster than standard display refresh rates. Yet the LEDs are also near-continuously detecting and absorbing light, and a display made of the LEDs can be programmed to respond to light signals in a number of ways.
For example, a display could automatically adjust brightness in response to ambient light conditions -- on a pixel-by-pixel basis.
"You can imagine sitting outside with your tablet, reading. Your tablet will detect the brightness and adjust it for individual pixels," Shim said. "Where there's a shadow falling across the screen it will be dimmer, and where it's in the sun it will be brighter, so you can maintain steady contrast."
The researchers demonstrated pixels that automatically adjust brightness, as well as pixels that respond to an approaching finger, which could be integrated into interactive displays that respond to touchless gestures or recognize objects.
They also demonstrated arrays that respond to a laser stylus, which could be the basis of smart whiteboards, tablets or other surfaces for writing or drawing with light. And the researchers found that the LEDs not only respond to light, but can convert it to electricity as well.
"The way it responds to light is like a solar cell. So not only can we enhance interaction between users and devices or displays, now we can actually use the displays to harvest light," Shim said. "So imagine your cellphone just sitting there collecting the ambient light and charging. That's a possibility without having to integrate separate solar cells. We still have a lot of development to do before a display can be completely self-powered, but we think that we can boost the power-harvesting properties without compromising LED performance, so that a significant amount of the display's power is coming from the array itself."
In addition to interacting with users and their environment, nanorod LED displays can interact with each other as large parallel communication arrays. It would be slower than device-to-device technologies like Bluetooth, Shim said, but those technologies are serial -- they can only send one bit at a time. Two LED arrays facing each other could communicate with as many bits as there are pixels in the screen.
"We primarily interface with our electronic devices through their displays, and a display's appeal resides in the user's experience of viewing and manipulating information," said study coauthor Peter Trefonas, a corporate fellow in Electronic Materials at the Dow Chemical Company. "The bidirectional capability of these new LED materials could enable devices to respond intelligently to external stimuli in new ways. The potential for touchless gesture control alone is intriguing, and we're only scratching the surface of what could be possible."
The researchers did all their demonstrations with arrays of red LEDs. They are now working on methods to pattern three-color displays with red, blue and green pixels, as well as working on ways to boost the light-harvesting capabilities by adjusting the composition of the nanorods.
###
This work was supported by a collaborative research effort between the Dow Chemical Company and the University of Illinois, with the aim of advancing technologies important to industry. The National Science Foundation also supported this work.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Liz Ahlberg Touchstone
217-244-1073
Copyright © University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
Thin films
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Display technology/LEDs/SS Lighting/OLEDs
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Efficient and stable hybrid perovskite-organic light-emitting diodes with external quantum efficiency exceeding 40 per cent July 5th, 2024
Efficient and stable hybrid perovskite-organic light-emitting diodes with external quantum efficiency exceeding 40 per cent July 5th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








