Home > Press > Nanoscale Modifications can be used to Engineer Electrical Contacts for Nanodevices
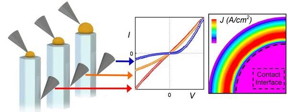 |
| Figure 1. Schematic diagram showing the electrical measurements performed on nanowires that have different sized Au particles (left) and the resultant current-voltage behaviour (centre) is controlled by geometrical effects that determine the magnitude of tunnelling current at the contact edge, shown by finite-element simulations (right). This effect is the basis for engineering the electrical contacts. Taken from open access reference 1. Image: Alex Lord/Swansea University. |
Abstract:
Scientists at Swansea University show nanoscale modifications to the edge region of nanocontacts to nanowires can be used to engineer the electrical transport process.
Nanoscale Modifications can be used to Engineer Electrical Contacts for Nanodevices
Swansea, UK | Posted on January 13th, 2017With the emergence of 1-d and 2-d nanostructures as the future of electronic materials there is a pressing need to develop new electrical contact preparation techniques that can refine the traditional processes for nanotechnological devices. The future of semiconductor devices brings significant challenges as the dimensions of the device components have been reduced from 3-d to 2-d, and now to 1-d. This research team, led by Prof. Wilks at Swansea University, is pursuing methods to engineer quantum based electrical contact technology to address the needs of the semiconductor industry as it develops devices based on nanomaterials.
Electrical contacts are essential components for any electrical device as they control the flow of electrical charge into and out of the device. When a lack of control over the final contact properties is present designing and optimising the system is impossible. Through decades of experimental and theoretical study a degree of control has been developed through band engineering when selecting contacts to large-scale planar devices such as field effect transistors. Before the advent of nanotechnology, semiconductor devices applied thin material layers to engineer interfaces and contacts, such as lasers using quantum wells, in which case the active layers could be considered 2-dimensional in nature. Now with the intense study of nanotubes, nanowires, nanorods, quantum wires, nanoribbons and many other materials the physics in some cases has been reduced to one dimension.
The current research project was expressed by Dr. Alex Lord, “New technologies based on these materials are emerging such as chemical and biological sensors, quantum computing, energy harvesting, lasers, and environmental- and photon-detectors. However, reliably engineering electrical contacts to these nanomaterials is essential to allow the development of nanoscience into a real-world technology and bring about the profound advances to the electronics industry that Scientists and Engineers know are possible.” The researcher notes that “traditional methods of engineering electrical contacts have been applied to nanomaterials but often neglect the nanoscale effects that nanoscientists have worked so hard to uncover. At the current time, a design toolbox to fabricate electrical contacts of chosen properties to nanomaterials is not close and research is lagging behind our potential application of the materials.”
The ability to define the contacts as Schottky or Ohmic with high or low resistance is complicated by the 2-d, 1-d or quasi 1-d nature of many nanomaterials and the restricted volume of material available for engineering. Traditional techniques to engineer the contact properties inevitably alter the nanomaterial properties because of the inherently large and exposed material surface.
Nanotechnology has delivered new materials and new technologies with applications of nanotechnology will continue to expand over the coming decades. Much of the usefulness stems from effects that occur at the atomic- or nano-scale. The lead researchers, Dr. Alex M. Lord and Prof. Steve Wilks at Swansea University, were motivated to “develop a deep understanding of unique effects at these length scales that occur in nanowires and to uncover synergistic relationships such as between metal nanocatalyst particles and nanowires”, said Alex Lord. There is a natural cross over between catalysts and electrical contacts because the behaviour of both can be heavily influenced by the surface properties of the material at the edge of the interface between the particle and support.
At Swansea University we have recently shown that the electrical transport of nanocatalyst contacts on nanowires can be controlled by varying the size of the metal particle in relation to the nanowire diameter, Figure 1, due to quantum-mechanical tunnelling at the contact edge.[1] This was confirmed in a newly-published study with UK collaborators Dr. Quentin Ramasse and Dr. Demie Kepaptsoglou at SuperSTEM, the EPSRC funded national facility for aberration-corrected STEM, UK, and also published in Nano Letters, that developed a new experimental process (eSTEM) to directly correlate atomic-resolution electron microscopy to transport measurements on single Au-nanowire interfaces.[2]
“The new experimental procedure has a simple premise but it was challenging to optimise and allow atomic scale imaging of the interfaces. It was essential to this study and will allow many more nanomaterials to be investigated in a similar way”, said Alex Lord who developed the experiments with Quentin Ramasse. eSTEM allowed the authors to confirm the quantum effects they described earlier by adding or removing material to the tunnelling channel at the interface edge that enhances or removes the tunnelling path. This powerful effect provides a simple method for controlling the electrical transport properties of the nanocontacts, summarised in Figure 2, that nanodevice engineers can exploit for many devices currently being developed such as nanowire biosensors.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Alex Lord
Copyright © Swansea University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








