Home > Press > The researchers created a tiny laser using nanoparticles
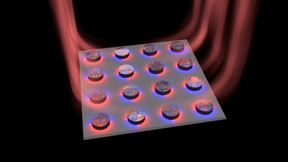 |
| The researchers at Aalto University have made an array of nanoparticles combined with dye molecules to act as a tiny laser. The lasing occurs in a dark mode and the laser light leaks out from the edges of array. CREDIT Antti Paraoanu |
Abstract:
Researchers at Aalto University, Finland are the first to develop a plasmonic nanolaser that operates at visible light frequencies and uses so-called dark lattice modes.
The researchers created a tiny laser using nanoparticles
Aalto, Finland | Posted on January 5th, 2017The laser works at length scales 1000 times smaller than the thickness of a human hair. The lifetimes of light captured in such small dimensions are so short that the light wave has time to wiggle up and down only a few tens or hundreds of times. The results open new prospects for on-chip coherent light sources, such as lasers, that are extremely small and ultrafast.
The laser operation in this work is based on silver nanoparticles arranged in a periodic array. In contrast to conventional lasers, where the feedback of the lasing signal is provided by ordinary mirrors, this nanolaser utilizes radiative coupling between silver nanoparticles. These 100-nanometer-sized particles act as tiny antennas. To produce high intensity laser light, the interparticle distance was matched with the lasing wavelength so that all particles of the array radiate in unison. Organic fluorescent molecules were used to provide the input energy (the gain) that is needed for lasing.
Light from the dark
A major challenge in achieving lasing this way was that light may not exist long enough in such small dimensions to be helpful. The researchers found a smart way around this potential problem: they produced lasing in dark modes.
"A dark mode can be intuitively understood by considering regular antennas: A single antenna, when driven by a current, radiates strongly, whereas two antennas -- if driven by opposite currents and positioned very close to each other -- radiate very little," explains Academy Professor Päivi Törmä. "A dark mode in a nanoparticle array induces similar opposite-phase currents in each nanoparticle, but now with visible light frequencies", she continues.
"Dark modes are attractive for applications where low power consumption is needed. But without any tricks, dark mode lasing would be quite useless because the light is essentially trapped at the nanoparticle array and cannot leave", adds staff scientist Tommi Hakala. "But by utilizing the small size of the array, we found an escape route for the light. Towards the edges of the array, the nanoparticles start to behave more and more like regular antennas that radiate to the outer world", tells Ph.D. student Heikki Rekola.
The research team used the nanofabrication facilities and cleanrooms of the national OtaNano research infrastructure.
The results have been published in the journal Nature Communications.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Paivi Torma
358-503-826-770
Copyright © Aalto University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() Quantum Dynamics research group:
Quantum Dynamics research group:
![]() Centre of Excellence in Computational Nanoscience, COMP:
Centre of Excellence in Computational Nanoscience, COMP:
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Wireless/telecommunications/RF/Antennas/Microwaves
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
Videos/Movies
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Optical computing/Photonic computing
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
![]() Nanophotonic platform boosts efficiency of nonlinear-optical quantum teleportation April 25th, 2025
Nanophotonic platform boosts efficiency of nonlinear-optical quantum teleportation April 25th, 2025
![]() Groundbreaking research unveils unified theory for optical singularities in photonic microstructures December 13th, 2024
Groundbreaking research unveils unified theory for optical singularities in photonic microstructures December 13th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








