Home > Press > Supersonic spray yields new nanomaterial for bendable, wearable electronics: Film of self-fused nanowires clear as glass, conducts like metal
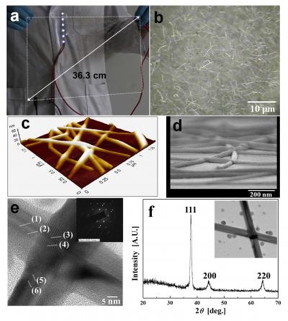 |
| Left, photograph of a large-scale silver nanowire-coated flexible film. Right, silver nanowire particles viewed under the microscope. CREDIT S.K. Yoon, Korea University |
Abstract:
A new, ultrathin film that is both transparent and highly conductive to electric current has been produced by a cheap and simple method devised by an international team of nanomaterials researchers from the University of Illinois at Chicago and Korea University.
Supersonic spray yields new nanomaterial for bendable, wearable electronics: Film of self-fused nanowires clear as glass, conducts like metal
Chicago, IL | Posted on November 23rd, 2016The film is also bendable and stretchable, offering potential applications in roll-up touchscreen displays, wearable electronics, flexible solar cells and electronic skin. The results are reported in Advanced Functional Materials.
The new film is made of fused silver nanowires, and is produced by spraying the nanowire particles through a tiny jet nozzle at supersonic speed. The result is a film with nearly the electrical conductivity of silver-plate -- and the transparency of glass, says senior author Alexander Yarin, UIC Distinguished Professor of Mechanical Engineering.
"The silver nanowire is a particle, but very long and thin," Yarin said. The nanowires measure about 20 microns long, so four laid end-to-end would span the width of a human hair. But their diameter is a thousand times smaller -- and significantly smaller than the wavelength of visible light, which minimizes light scattering.
The researchers suspended the nanowire particles in water and propelled them by air through a de Laval nozzle, which has the same geometry as a jet engine, but is only a few millimeters in diameter.
"The liquid needs to be atomized so it evaporates in flight," Yarin said. When the nanowires strike the surface they are being applied to at supersonic speed, they fuse together, as their kinetic energy is converted to heat.
"The ideal speed is 400 meters per second," Yarin said. "If the energy is too high, say 600 meters per second, it cuts the wires. If too low, as at 200 meters per second, there's not enough heat to fuse the wires."
The researchers applied the nanowires to flexible plastic films and to three-dimensional objects. "The surface shape doesn't matter," Yarin said.
The transparent flexible film can be bent repeatedly and stretched to seven times its original length and still work, said Sam Yoon, the corresponding author of the study and a professor of mechanical engineering at Korea University.
Earlier this year, Yarin and Yoon and their colleagues produced a transparent conducting film by electroplating a mat of tangled nanofiber with copper. Compared to that film, the self-fused silver nanowire film offers better scalability and production rate, Yoon said.
"It should be easier and cheaper to fabricate, as it's a one-step versus a two-step process," said Yarin. "You can do it roll-to-roll on an industrial line, continuously."
###
Co-authors with Yarin and Yoon are Jong-Gun Lee, Do-Yeon Kim, Jong-Hyuk Lee and Donghwan Kim of Korea University; Suman Sinha-Ray of the Indian Institute of Technology in Indore, India; and Mark T. Swihart of the State University of New York at Buffalo.
The research was supported by the National Research Foundation, GFHIM-2013M3A6B1078879, and the Industrial Strategic Technology Development Program, 10045221, funded by the Ministry of Knowledge Economy of Korea.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Bill Burton
312-996-2269
Copyright © University of Illinois at Chicago
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Flexible Electronics
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() Flexible electronics integrated with paper-thin structure for use in space January 17th, 2025
Flexible electronics integrated with paper-thin structure for use in space January 17th, 2025
Wearable electronics
![]() Breakthrough brings body-heat powered wearable devices closer to reality December 13th, 2024
Breakthrough brings body-heat powered wearable devices closer to reality December 13th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Nanoelectronics
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
![]() Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
![]() Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Industrial
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() Quantum interference in molecule-surface collisions February 28th, 2025
Quantum interference in molecule-surface collisions February 28th, 2025
![]() Boron nitride nanotube fibers get real: Rice lab creates first heat-tolerant, stable fibers from wet-spinning process June 24th, 2022
Boron nitride nanotube fibers get real: Rice lab creates first heat-tolerant, stable fibers from wet-spinning process June 24th, 2022
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








