Home > Press > Tooth decay -- drilling down to the nanoscale: Researchers from the University of Sydney believe they have identified some nanoscale elements that govern the behavior of our teeth
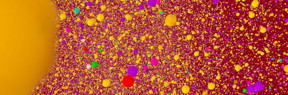 |
| Magnesium in enamel at atomic scale is shown. CREDIT: Tom Hartley - University of Sydney |
Abstract:
With one in two Australian children reported to have tooth decay in their permanent teeth by age 12, researchers from the University of Sydney believe they have identified some nanoscale elements that govern the behaviour of our teeth.
Tooth decay -- drilling down to the nanoscale: Researchers from the University of Sydney believe they have identified some nanoscale elements that govern the behavior of our teeth
Sydney, Australia | Posted on September 11th, 2016Material and structures engineers worked with dentists and bioengineers to map the exact composition and structure of tooth enamel at the atomic scale.
Using a relatively new microscopy technique called atom probe tomography, their work produced the first-ever three-dimensional maps showing the positions of atoms critical in the decay process.
The new knowledge on atom composition at the nanolevel has the potential to aid oral health hygiene and caries prevention, and has been published today in the journal Science Advances.
Professor Julie Cairney, Material and Structures Engineer in the Faculty of Engineering and Information Technologies, said:
"The dental professionals have known that certain trace ions are important in the tough structure of tooth enamel but until now it had been impossible to map the ions in detail.
"The structure of human tooth enamel is extremely intricate and while we have known that magnesium, carbonate and fluoride ions influence enamel properties scientists have never been able to capture its structure at a high enough resolution or definition."
"What we have found are the magnesium-rich regions between the hydroxyapatite nanorods that make up the enamel.
"This means we have the first direct evidence of the existence of a proposed amorphous magnesium-rich calcium phosphate phase that plays an essential role in governing the behaviour of teeth. "
Co-lead researcher on the study, Dr Alexandre La Fontaine from the University's Australian Centre for Microscopy and Microanalysis, said:
We were also able to see nanoscale 'clumps' of organic material, which indicates that proteins and peptides are heterogeneously distributed within the enamel rather than present along all the nanorod interfaces, which was what was previously suggested.
The mapping has the potential for new treatments designed around protecting against the dissolution of this specific amorphous phase.
The new understanding of how enamel forms will also help in tooth remineralisation research."
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Victoria Hollick
040-171-1361
Copyright © University of Sydney
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Dental
![]() Innovations in dentistry: Navigational surgery, robotics, and nanotechnology October 2nd, 2020
Innovations in dentistry: Navigational surgery, robotics, and nanotechnology October 2nd, 2020
![]() First measurement of electron energy distributions, could enable sustainable energy technologies June 5th, 2020
First measurement of electron energy distributions, could enable sustainable energy technologies June 5th, 2020
![]() Gas storage method could help next-generation clean energy vehicles: Tremendous amounts of hydrogen and methane can be stored in nanoscopic pores April 17th, 2020
Gas storage method could help next-generation clean energy vehicles: Tremendous amounts of hydrogen and methane can be stored in nanoscopic pores April 17th, 2020
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








