Home > Press > Legions of nanorobots target cancerous tumors with precision: Administering anti-cancer drugs redefined
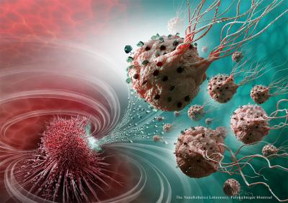 |
| The legions of nanorobotic agents are actually composed of more than 100 million flagellated bacteria -- and therefore self-propelled -- and loaded with drugs that moved by taking the most direct path between the drug's injection point and the area of the body to cure. CREDIT: Montréal Nanorobotics Laboratory |
Abstract:
Researchers from Polytechnique Montréal, Université de Montréal and McGill University have just achieved a spectacular breakthrough in cancer research. They have developed new nanorobotic agents capable of navigating through the bloodstream to administer a drug with precision by specifically targeting the active cancerous cells of tumours. This way of injecting medication ensures the optimal targeting of a tumour and avoids jeopardizing the integrity of organs and surrounding healthy tissues. As a result, the drug dosage that is highly toxic for the human organism could be significantly reduced.
Legions of nanorobots target cancerous tumors with precision: Administering anti-cancer drugs redefined
Montreal, Canada | Posted on August 16th, 2016This scientific breakthrough has just been published in the prestigious journal Nature Nanotechnology in an article titled "Magneto-aerotactic bacteria deliver drug-containing nanoliposomes to tumour hypoxic regions." The article notes the results of the research done on mice, which were successfully administered nanorobotic agents into colorectal tumours.
"These legions of nanorobotic agents were actually composed of more than 100 million flagellated bacteria - and therefore self-propelled - and loaded with drugs that moved by taking the most direct path between the drug's injection point and the area of the body to cure," explains Professor Sylvain Martel, holder of the Canada Research Chair in Medical Nanorobotics and Director of the Polytechnique Montréal Nanorobotics Laboratory, who heads the research team's work. "The drug's propelling force was enough to travel efficiently and enter deep inside the tumours."
When they enter a tumour, the nanorobotic agents can detect in a wholly autonomous fashion the oxygen-depleted tumour areas, known as hypoxic zones, and deliver the drug to them. This hypoxic zone is created by the substantial consumption of oxygen by rapidly proliferative tumour cells. Hypoxic zones are known to be resistant to most therapies, including radiotherapy.
But gaining access to tumours by taking paths as minute as a red blood cell and crossing complex physiological micro-environments does not come without challenges. So Professor Martel and his team used nanotechnology to do it.
Bacteria with compass
To move around, bacteria used by Professor Martel's team rely on two natural systems. A kind of compass created by the synthesis of a chain of magnetic nanoparticles allows them to move in the direction of a magnetic field, while a sensor measuring oxygen concentration enables them to reach and remain in the tumour's active regions. By harnessing these two transportation systems and by exposing the bacteria to a computer-controlled magnetic field, researchers showed that these bacteria could perfectly replicate artificial nanorobots of the future designed for this kind of task.
"This innovative use of nanotransporters will have an impact not only on creating more advanced engineering concepts and original intervention methods, but it also throws the door wide open to the synthesis of new vehicles for therapeutic, imaging and diagnostic agents," Professor Martel adds. "Chemotherapy, which is so toxic for the entire human body, could make use of these natural nanorobots to move drugs directly to the targeted area, eliminating the harmful side effects while also boosting its therapeutic effectiveness."
###
The work by Professor Martel obtained the very valuable support of the Consortium québécois sur la découverte du médicament (Québec consortium for drug discovery - CQDM), the Canada Research Chairs, the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC), the Research Chair in Nanorobotics of Polytechnique Montréal, Mitacs, the Canada Foundation for Innovation (CFI) and the National Institutes of Health (NIH). Montréal's Jewish General Hospital, the McGill University Health Centre (MUHC), the Institute for Research in Immunology and Cancer (IRIC), and the Rosalind and Morris Goodman Cancer Research Centre also took part in this promising research work.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Annie Touchette
514-231-8133
Copyright © Polytechnique Montréal
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
Magnetism/Magnons
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Cancer
Robotics
![]() Nanofibrous metal oxide semiconductor for sensory face November 8th, 2024
Nanofibrous metal oxide semiconductor for sensory face November 8th, 2024
![]() Femtosecond laser technique births "dancing microrobots": USTC's breakthrough in multi-material microfabrication August 11th, 2023
Femtosecond laser technique births "dancing microrobots": USTC's breakthrough in multi-material microfabrication August 11th, 2023
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Molecular Machines
![]() First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
![]() Nanotech scientists create world's smallest origami bird March 17th, 2021
Nanotech scientists create world's smallest origami bird March 17th, 2021
![]() Giant nanomachine aids the immune system: Theoretical chemistry August 28th, 2020
Giant nanomachine aids the immune system: Theoretical chemistry August 28th, 2020
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








