Home > Press > Making magnets flip like cats at room temperature: Heusler alloy NiMnSb could prove valuable as a new material for digital information processing and storage
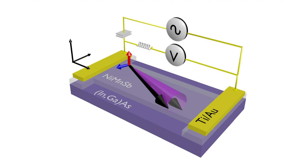 |
| This image shows a flipping NiMnSb magnet. CREDIT: ill.:/©: Inspire Group, JGU |
Abstract:
In today's world of ever-increasing digital information storage and computation, the next information storage revolution seeks to exploit a novel effect arising from the relativistic physics of Einstein which allows to make a new type of magnet behave like cats. Similar to the ability of a cat to flip itself in the air by twisting different parts of its body in different directions and land on its feet, these magnets can flip themselves through the internal motion of their own electrons. "In these new magnetic materials, a current running through the magnet can turn around the direction of the magnetization depending on the direction of the current," explained Professor Jairo Sinova of the Institute of Physics at Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU). "This novel phenomenon in physics, dubbed spin-orbit torques, links the spin-degree of freedom of magnets which gives rise to the magnetization to the charge degree of freedom that allows for current-charge motion inside the material.
Making magnets flip like cats at room temperature: Heusler alloy NiMnSb could prove valuable as a new material for digital information processing and storage
Mainz, Germany | Posted on July 25th, 2016This novel effect has been pioneered, among others, by recent predictions by the Sinova group in Mainz together with theoretical and experimental collaborators. It occurs in magnetic materials that have broken-inversion symmetry. The researchers first observed spin-orbit torques in the artificial bulk diluted magnetic semiconductor GaMnAs. GaMnAs is the diluted counterpart of crystalline zincblende structures of Silicon and Gallium arsenide, which are the pillars of modern electronics. However, in GaMnAs, spin-orbit torques were demonstrated only at very low temperatures.
In collaboration with an international team of researchers from Prague, Cambridge, Würzburg, Jülich, and Nottingham, Professor Jairo Sinova and his Ph.D. students Jacob Gayles and Libor Šmejkal now have published their findings, which could pave the way for using spin-orbit torques in technological applications. Thanks to the synergetic teamwork of theorists and experimentalists, the researchers were able to predict and demonstrate the effect of spin-orbit torques in NiMnSb crystal at room temperature. NiMnSb was chosen according to the systematic analysis of the symmetry the crystal point groups in conjunction with microscopic first principles calculations of the effect. All electrical ferromagnetic resonance measurements were then used to detect the room-temperature spin-orbit torques in NiMnSb microbars. Being able to use single magnet manipulation at room temperature represents an important step towards improved magnetic random access memory architectures for technical applications that are all fully electrical, highly scalable, and require low power.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Dr. Jairo Sinova
49-613-139-23646
Copyright © Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
Magnetism/Magnons
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Memory Technology
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Nanoelectronics
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
![]() Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
![]() Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








