Home > Press > Discovery could dramatically boost efficiency of perovskite solar cells: Nanoscale images by Berkeley Lab researchers yield surprise that could push efficiency to 31 percent
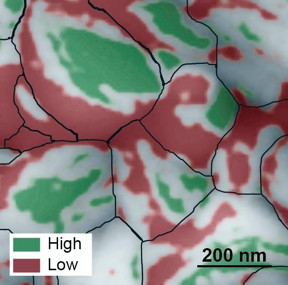 |
| This atomic force microscopy image of the grainy surface of a perovskite solar cell reveals a new path to much greater efficiency. Individual grains are outlined in black, low-performing facets are red, and high-performing facets are green. A big jump in efficiency could possibly be obtained if the material can be grown so that more high-performing facets develop. CREDIT:Berkeley Lab |
Abstract:
Scientists from the Department of Energy's Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) have discovered a possible secret to dramatically boosting the efficiency of perovskite solar cells hidden in the nanoscale peaks and valleys of the crystalline material.
Discovery could dramatically boost efficiency of perovskite solar cells: Nanoscale images by Berkeley Lab researchers yield surprise that could push efficiency to 31 percent
Berkeley, CA | Posted on July 6th, 2016Solar cells made from compounds that have the crystal structure of the mineral perovskite have captured scientists' imaginations. They're inexpensive and easy to fabricate, like organic solar cells. Even more intriguing, the efficiency at which perovskite solar cells convert photons to electricity has increased more rapidly than any other material to date, starting at three percent in 2009 -- when researchers first began exploring the material's photovoltaic capabilities -- to 22 percent today. This is in the ballpark of the efficiency of silicon solar cells.
Now, as reported online July 4, 2016 in the journal Nature Energy, a team of scientists from the Molecular Foundry and the Joint Center for Artificial Photosynthesis, both at Berkeley Lab, found a surprising characteristic of a perovskite solar cell that could be exploited for even higher efficiencies, possibly up to 31 percent.
Using photoconductive atomic force microscopy, the scientists mapped two properties on the active layer of the solar cell that relate to its photovoltaic efficiency. The maps revealed a bumpy surface composed of grains about 200 nanometers in length, and each grain has multi-angled facets like the faces of a gemstone.
Unexpectedly, the scientists discovered a huge difference in energy conversion efficiency between facets on individual grains. They found poorly performing facets adjacent to highly efficient facets, with some facets approaching the material's theoretical energy conversion limit of 31 percent.
The scientists say these top-performing facets could hold the secret to highly efficient solar cells, although more research is needed.
"If the material can be synthesized so that only very efficient facets develop, then we could see a big jump in the efficiency of perovskite solar cells, possibly approaching 31 percent," says Sibel Leblebici, a postdoctoral researcher at the Molecular Foundry.
Leblebici works in the lab of Alexander Weber-Bargioni, who is a corresponding author of the paper that describes this research. Ian Sharp, also a corresponding author, is a Berkeley Lab scientist at the Joint Center for Artificial Photosynthesis. Other Berkeley Lab scientists who contributed include Linn Leppert, Francesca Toma, and Jeff Neaton, the director of the Molecular Foundry.
A team effort
The research started when Leblebici was searching for a new project. "I thought perovskites are the most exciting thing in solar right now, and I really wanted to see how they work at the nanoscale, which has not been widely studied," she says.
She didn't have to go far to find the material. For the past two years, scientists at the nearby Joint Center for Artificial Photosynthesis have been making thin films of perovskite-based compounds, and studying their ability to convert sunlight and CO2 into useful chemicals such as fuel. Switching gears, they created pervoskite solar cells composed of methylammonium lead iodide. They also analyzed the cells' performance at the macroscale.
The scientists also made a second set of half cells that didn't have an electrode layer. They packed eight of these cells on a thin film measuring one square centimeter. These films were analyzed at the Molecular Foundry, where researchers mapped the cells' surface topography at a resolution of ten nanometers. They also mapped two properties that relate to the cells' photovoltaic efficiency: photocurrent generation and open circuit voltage.
This was performed using a state-of-the-art atomic force microscopy technique, developed in collaboration with Park Systems, which utilizes a conductive tip to scan the material's surface. The method also eliminates friction between the tip and the sample. This is important because the material is so rough and soft that friction can damage the tip and sample, and cause artifacts in the photocurrent.
Surprise discovery could lead to better solar cells
The resulting maps revealed an order of magnitude difference in photocurrent generation, and a 0.6-volt difference in open circuit voltage, between facets on the same grain. In addition, facets with high photocurrent generation had high open circuit voltage, and facets with low photocurrent generation had low open circuit voltage.
"This was a big surprise. It shows, for the first time, that perovskite solar cells exhibit facet-dependent photovoltaic efficiency," says Weber-Bargioni.
Adds Toma, "These results open the door to exploring new ways to control the development of the material's facets to dramatically increase efficiency."
In practice, the facets behave like billions of tiny solar cells, all connected in parallel. As the scientists discovered, some cells operate extremely well and others very poorly. In this scenario, the current flows towards the bad cells, lowering the overall performance of the material. But if the material can be optimized so that only highly efficient facets interface with the electrode, the losses incurred by the poor facets would be eliminated.
"This means, at the macroscale, the material could possibly approach its theoretical energy conversion limit of 31 percent," says Sharp.
A theoretical model that describes the experimental results predicts these facets should also impact the emission of light when used as an LED. Linn Leppert, Sebastian Reyes-Lillo, and Jeff Neaton performed this particular work.
The Molecular Foundry is a DOE Office of Science User Facility located at Berkeley Lab. The Joint Center for Artificial Photosynthesis is a DOE Energy Innovation Hub led by the California Institute of Technology in partnership with Berkeley Lab.
###
The research was supported in part by the Department of Energy's Office of Science.
####
About Berkeley Lab
Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory addresses the world's most urgent scientific challenges by advancing sustainable energy, protecting human health, creating new materials, and revealing the origin and fate of the universe. Founded in 1931, Berkeley Lab's scientific expertise has been recognized with 13 Nobel prizes. The University of California manages Berkeley Lab for the U.S. Department of Energy's Office of Science. For more, visit http://www.lbl.gov.
DOE's Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the Unites States, and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, please visit the Office of Science website at science.energy.gov.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Dan Krotz
510-486-4019
Copyright © Berkeley Lab
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
![]() Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








