Home > Press > CWRU physicists deploy magnetic vortex to control electron spin: Potential technology for quantum computing, keener sensors
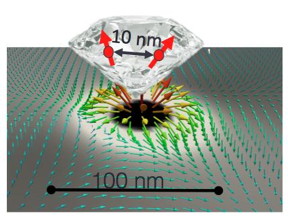 |
| Researchers coupled a diamond nanoparticle with a magnetic vortex to control electron spin in nitrogen-vacancy defects. CREDIT: Case Western Reserve University |
Abstract:
Researchers at Case Western Reserve University have developed a way to swiftly and precisely control electron spins at room temperature.
CWRU physicists deploy magnetic vortex to control electron spin: Potential technology for quantum computing, keener sensors
Cleveland, OH | Posted on June 21st, 2016The technology, described in Nature Communications, offers a possible alternative strategy for building quantum computers that are far faster and more powerful than today's supercomputers.
"What makes electronic devices possible is controlling the movement of electrons from place to place using electric fields that are strong, fast and local," said physics Professor Jesse Berezovsky, leader of the research. "That's hard with magnetic fields, but they're what you need to control spin."
Other researchers have searched for materials where electric fields can mimic the effects of a magnetic field, but finding materials where this effect is strong enough and still works at room temperature has proven difficult.
"Our solution," Berezovsky said, "is to use a magnetic vortex."
Berezovsky worked with physics PhD students Michael S. Wolf and Robert Badea.
The researchers fabricated magnetic micro-disks that have no north and south poles like those on a bar magnet, but magnetize into a vortex. A magnetic field emanates from the vortex core. At the center point, the field is particularly strong and rises perpendicular to the disk.
The vortices are coupled with diamond nanoparticles. In the diamond lattice inside each nanoparticle, several individual spins are trapped inside of defects called nitrogen vacancies.
The scientists use a pulse from a laser to initialize the spin. By applying microwaves and a weak magnetic field, Berezovsky's team can move the vortex in nanoseconds, shifting the central point, which can cause an electron to change its spin.
In what's called a quantum coherent state, the spin can act as a quantum bit, or qubit--the basic unit of information in a quantum computer,
In current computers, bits of information exist in one of two states: zero or one. But in a superposition state, the spin can be up and down at the same time, that is, zero and one simultaneously. That capability would allow for more complex and faster computing.
"The spins are close to each other; you want spins to interact with their neighbors in quantum computing," Berezovsky said. "The power comes from entanglement."
The magnetic field gradient produced by a vortex proved sufficient to manipulate spins just nanometers apart.
In addition to computing, electrons controlled in coherent quantum states might be useful for extremely high-resolution sensors, the researchers say. For example, in an MRI, they could be used to sense magnetic fields in far more detail than with today's technology, perhaps distinguishing atoms.
Controlling the electron spins without destroying the coherent quantum states has proven difficult with other techniques, but a series of experiments by the group has shown the quantum states remain solid. In fact, "the vortex appears to enhance the microwave field we apply," Berezovsky said.
The scientists are continuing to shorten the time it takes to change the spin, which is a key to high-speed computing. They are also investigating the interactions between the vortex, microwave magnetic field and electron spin, and how they evolve together.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Kevin Mayhood
216-534-7183
Copyright © Case Western Reserve University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
Magnetism/Magnons
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Quantum Physics
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Spintronics
![]() Quantum materials: Electron spin measured for the first time June 9th, 2023
Quantum materials: Electron spin measured for the first time June 9th, 2023
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Quantum Computing
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Quantum nanoscience
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








