Home > Press > A new-structure magnetic memory device developed
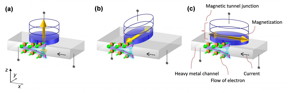 |
| Schematics of structures for three kinds of spin-orbit-torque-induced magnetization scheme. (a) The first previous structure where the magnetization is perpendicular to the film plane. (b) The second previous structure where the magnetization is in-plane and orthogonal to channel current. (c) The new structure where the magnetization is in-plane and collinear with the current. CREDIT: Shunsuke Fukami |
Abstract:
The research group of Professor Hideo Ohno and Associate Professor Shunsuke Fukami of Tohoku University has developed a new-structure magnetic memory device utilizing spin-orbit- torque-induced magnetization switching.
A new-structure magnetic memory device developed
Sendai, Japan | Posted on March 24th, 2016For these two decades, much effort has been devoted to the development of magnetic random access memories (MRAMs), which store information as the magnetization direction of a magnet. Since the magnetization can, be in general, be reversed at high speed unlimitedly, the MRAMs are regarded as a promising replacement for currently-used semiconductor-based working memories such as static random access memories (SRAMs) and dynamic random access memories (DRAMs), which are now facing several serious issues.
The central issue of the MRAM development is how to achieve magnetization reversal efficiently.
Recently, spin-orbit-torque (SOT)-induced magnetization switching - where torques brought about by an in-plane current through the spin-orbit interactions are utilized - was demonstrated and intensively studied. In principle, the SOT-induced switching allows for an ultrafast magnetization reversal in a nanosecond timescale.
The research group of Tohoku University showed a new scheme of SOT-induced magnetization switching. Whereas there had been two kinds of switching schemes where the magnetization is directed orthogonally to the applied write current, the present structure has the magnetization directing collinear with the current. The group fabricated three-terminal devices with the new structure, where a Ta/CoFeB/MgO-based magnetic tunnel junction is used, and successfully demonstrated the switching operation.
The required current density to induce the magnetization switching was reasonably small and the resistance difference between "0" and "1" states was reasonably large, indicating that the new structure is a promising candidate for the MRAM applications.
In addition, the group showed that the new structure has the potential to serve as a useful tool to go deeply into the physics of SOT-induced switching, in which a number of unrevealed issues remain.
The magnetic memory device can store the information without power supply, allowing a drastic reduction of the power consumption of integrated circuits. In particular, this benefit becomes significant for applications that have relatively long standby times, such as sensor nodes which are likely to perform important roles in future IoT (Internet of Things) societies.
In this regard, the present work is expected to pave the way toward the realization of ultralow-power and high-performance integrated circuits and IoT societies.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Shunsuke Fukami
Copyright © Tohoku University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
Magnetism/Magnons
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Internet-of-Things
![]() Nanofibrous metal oxide semiconductor for sensory face November 8th, 2024
Nanofibrous metal oxide semiconductor for sensory face November 8th, 2024
![]() New nanowire sensors are the next step in the Internet of Things January 6th, 2023
New nanowire sensors are the next step in the Internet of Things January 6th, 2023
![]() New chip ramps up AI computing efficiency August 19th, 2022
New chip ramps up AI computing efficiency August 19th, 2022
![]() Lightening up the nanoscale long-wavelength optoelectronics May 13th, 2022
Lightening up the nanoscale long-wavelength optoelectronics May 13th, 2022
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Memory Technology
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








