Home > Press > Scientists suggest a 100 times faster type of memory cell based on superconductors
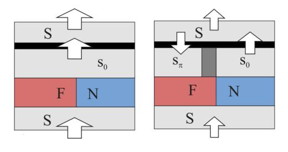 |
| Superconducting currents during reading various states of the memory cell are shown. The greater current the larger arrow. CREDIT: Authors of the study |
Abstract:
A group of scientists from Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology and from the Moscow State University has developed a fundamentally new type of memory cell based on superconductors - this type of memory will be able to work hundreds of times faster than the types of memory devices commonly used today, according to an article published in the journal Applied Physics Letters.
Scientists suggest a 100 times faster type of memory cell based on superconductors
Moscow, Russia | Posted on March 17th, 2016"With the operational function that we have proposed in these memory cells, there will be no need for time-consuming magnetization and demagnetization processes. This means that read and write operations will take only a few hundred picoseconds, depending on the materials and the geometry of the particular system, while conventional methods take hundreds or thousands of times longer than this," said the corresponding author of the study, Alexander Golubov, the Head of MIPT's Laboratory of Quantum Topological Phenomena in Superconducting Systems.
Golubov and his colleagues have proposed creating basic memory cells based on quantum effects in "sandwiches" of a superconductor - dielectric (or other insulating material) - superconductor, which were predicted in the 1960s by the British physicist Brian Josephson. The electrons in these "sandwiches" (they are called "Josephson junctions") are able to tunnel from one layer of a superconductor to another, passing through the dielectric like balls passing through a perforated wall.
Today, Josephson junctions are used both in quantum devices and conventional devices. For example, superconducting qubits are used to build the D-wave quantum system, which is capable of finding the minima of complex functions using the quantum annealing algorithm. There are also ultra-fast analogue-to-digital converters, devices to detect consecutive events, and other systems that do not require fast access to large amounts of memory. There have also been attempts to use the Josephson Effect to create ordinary processors. An experimental processor of this type was created in Japan in the late 1980s. In 2014, the research agency IAPRA resumed its attempts to create a prototype of a superconducting computer.
Josephson junctions with ferromagnets used as the middle of the "sandwich" are currently of greatest practical interest. In memory elements that are based on ferromagnets the information is encoded in the direction of the magnetic field vector in the ferromagnet. However, there are two fundamental flaws with this process: firstly, the low density of the "packaging" of the memory elements - additional chains need to be added to provide extra charge for the cells when reading or writing data, and secondly the magnetization vector cannot be changed quickly, which limits the writing speed.
The group of physicists from MIPT and MSU proposed encoding the data in Josephson cells in the value of the superconducting current. By studying the superconductor-normal metal/ferromagnet-superconductor-insulator-superconductor junctions, the scientists discovered that in certain longitudinal and transverse dimensions the layers of the system may have two energy minima, meaning they are in one of two different states. These two minima can be used to record data - zeros and ones.
In order to switch the system from "zero" to "one" and back again, the scientists have suggested using injection currents flowing through one of the layers of the superconductor. They propose to read the status using the current that flows through the whole structure. These operations can be performed hundreds of times faster than measuring the magnetization or magnetization reversal of a ferromagnet.
"In addition, our method requires only one ferromagnetic layer, which means that it can be adapted to so-called single flux quantum logic circuits, and this means that there will be no need to create an entirely new architecture for a processor. A computer based on single flux quantum logic can have a clock speed of hundreds of gigahertz, and its power consumption will be dozens of times lower," said Golubov.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Valerii Roizen
929-992-2721
Copyright © Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
Superconductivity
News and information
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Magnetism/Magnons
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Chip Technology
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Memory Technology
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Announcements
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








