Home > Press > Nature Materials: Smallest lattice structure worldwide: 3-D lattice with glassy carbon struts and braces of less than 200 nm in diameter has higher specific strength than most solids
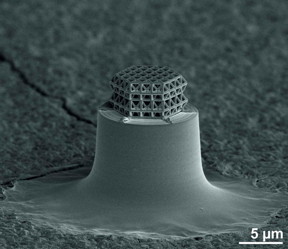 |
| The smallest lattice in the world is visible under the microscope only. Struts and braces are 0.2 µm in diameter. Total size of the lattice is about 10 µm.
Photo: J. Bauer / KIT |
Abstract:
KIT scientists now present the smallest lattice structure made by man in the Nature Materials journal. Its struts and braces are made of glassy carbon and are less than 1 µm long and 200 nm in diameter. They are smaller than comparable metamaterials by a factor of 5. The small dimension results in so far unreached ratios of strength to density. Applications as electrodes, filters or optical components might be possible. (DOI: 10.1038/nmat4561)
Nature Materials: Smallest lattice structure worldwide: 3-D lattice with glassy carbon struts and braces of less than 200 nm in diameter has higher specific strength than most solids
Karlsruhe, Germany | Posted on February 3rd, 2016"Lightweight construction materials, such as bones and wood, are found everywhere in nature," Dr.-Ing. Jens Bauer of Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT), the first author of the study, explains. "They have a high load-bearing capacity and small weight and, hence, serve as models for mechanical metamaterials for technical applications."
Metamaterials are materials, whose structures of some micrometers (millionths of a meter) in dimension are planned and manufactured specifically for them to possess mechanical or optical properties that cannot be reached by unstructured solids. Examples are invisibility cloaks that guide light, sound or heat around objects, materials that counterintuitively react to pressure and shear (auxetic materials) or lightweight nanomaterials of high specific stability (force per unit area and density).
The smallest stable lattice structure worldwide presented now was produced by the established 3D laser lithography process at first. The desired structure of micrometer size is hardened in a photoresist by laser beams in a computer-controlled manner. However, resolution of this process is limited, such that struts of about 5 - 10 µm length and 1 µm in diameter can be produced only. In a subsequent step, the structure was therefore shrunk and vitrified by pyrolysis. For the first time, pyrolysis was used for manufacturing microstructured lattices. The object is exposed to temperatures of around 900°C in a vacuum furnace. As a result, chemical bonds reorient themselves. Except for carbon, all elements escape from the resist. The unordered carbon remains in the shrunk lattice structure in the form of glassy carbon. The resulting structures were tested for stability under pressure by the researchers.
"According to the results, load-bearing capacity of the lattice is very close to the theoretical limit and far above that of unstructured glassy carbon," Prof. Oliver Kraft, co-author of the study, reports. Until the end of last year, Kraft headed the Institute for Applied Materials of KIT. This year, he took over office as KIT Vice President for Research. "Diamond is the only solid having a higher specific stability."
Microstructured materials are often used for insulation or shock absorption. Open-pored materials may be used as filters in chemical industry. Metamaterials also have extraordinary optical properties that are applied in telecommunications. Glassy carbon is a high-technology material made of pure carbon. It combines glassy, ceramic properties with graphite properties and is of interest for use in electrodes of batteries or electrolysis systems.
####
About Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT)
arlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) pools its three core tasks of research, higher education, and innovation in a mission. With about 9,400 employees and 25,000 students, KIT is one of the big institutions of research and higher education in natural sciences and engineering in Europe.
KIT - The Research University in the Helmholtz Association
Since 2010, the KIT has been certified as a family-friendly university.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Monika Landgraf
49-721-608-47414
For further information, please contact:
Kosta Schinarakis, PKM - Science Scout
Phone: +49 721 608 41956
Fax: +49 721 608 43658
Copyright © Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT)
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
Chemistry
![]() Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Single-atom catalysts change spin state when boosted by a magnetic field June 4th, 2025
Single-atom catalysts change spin state when boosted by a magnetic field June 4th, 2025
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Wireless/telecommunications/RF/Antennas/Microwaves
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Industrial
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() Quantum interference in molecule-surface collisions February 28th, 2025
Quantum interference in molecule-surface collisions February 28th, 2025
![]() Boron nitride nanotube fibers get real: Rice lab creates first heat-tolerant, stable fibers from wet-spinning process June 24th, 2022
Boron nitride nanotube fibers get real: Rice lab creates first heat-tolerant, stable fibers from wet-spinning process June 24th, 2022
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








