Home > Press > Spin current on topological insulator detected electrically at room temperature
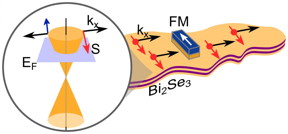 |
| This image shows the schematics of the spin current on a topological insulator surface, with the spin direction (S) perpendicular to the current direction (kx). The zoom in schematic shows the electronic band structure on the surface of the topological insulator. The spin polarization on topological insulator surface is electrically probed by a ferromagnetic tunnel contact (FM). CREDIT: André Dankert |
Abstract:
Researchers at Chalmers University of Technology have for the first time reported the electrical detection of spin current on topological insulator surfaces at room temperature by employing a ferromagnetic detector. The findings have been published in the journal Nano Letters.
Spin current on topological insulator detected electrically at room temperature
Gothenburg, Sweden | Posted on December 8th, 2015Solid-state materials were conventionally divided into three different classes such as conductors, semiconductors and insulators. Recently, a new class of materials has been proposed and realized, called "topological insulators", where both the insulating and conducting properties can co-exist in the same material.
Topological insulators are insulators inside the bulk, but are conducting on their surfaces with less resistance than the conventional materials. This is possible due to their uniquely strong interaction between electrons' spin and orbital angular momentum with their time reversal symmetry. The interaction is so strong that the spin angular momentum of the electrons is locked perpendicular to their momentum, and generates a spontaneous spin polarized current on the surfaces of topological insulators by applying an electric field.
These spin polarized conducting electrons on the surface have no mass and are extremely robust against most perturbations from defects or impurities, and can enable the propagation of dissipationless spin currents.
The researchers from Chalmers detected the surface spin current electrically on a topological insulator called bismuth selenide (Bi2Se3) for the first time at room temperature employing ferromagnetic tunnel contacts. Such contacts are known to be very sensitive to spin polarization and probe the Bi2Se3 surface by measuring the magnetoresistance due to parallel and anti-parallel alignment of the spin current and the ferromagnet magnetization direction.
"The key factors for these room temperature results are good quality topological insulator crystals and spin sensitive ferromagnetic tunnel contacts carefully prepared by clean room nanofabrication", explains Dr. André Dankert, the lead author of the paper.
Earlier reports in this research field were limited only to measurements at cryogenic temperatures. From the results on the magnitude of the spin signal, its sign, and control experiments, using different measurement configurations, angles and interface conditions, the author's rule out other known physical effects.
"Our results show the electrical accessibility of spin currents on topological insulator surfaces up to room temperature and pave the way for further developments, which can be useful for spin based information processing in the future", says associate professor Saroj Dash, who leads the research group.
However, Saroj Dash cautions that the research on development of these new class materials and measurement techniques are still in its early stage and more experiments are required for further understanding.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Johanna Wilde
46-317-722-029
Copyright © Chalmers University of Technology
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Spintronics
![]() Quantum materials: Electron spin measured for the first time June 9th, 2023
Quantum materials: Electron spin measured for the first time June 9th, 2023
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Quantum Computing
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








