Home > Press > Nanotube letters spell progress: Rice team characterizes, analyzes stiffness of individual branching nanotubes
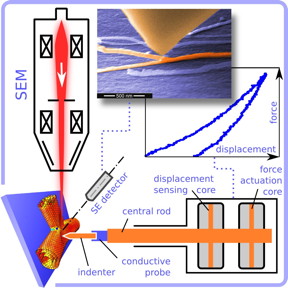 |
| Rice University researchers tested the stiffness of individual nanotube junctions with a combined scanning electron microscope and picoindenter. It allowed them to analyze nanotubes in real time. Credit: Evgeni Penev/Rice University |
Abstract:
Never mind the ABCs. Rice University scientists interested in nanotubes are studying their XYΩs.
Nanotube letters spell progress: Rice team characterizes, analyzes stiffness of individual branching nanotubes
Houston, TX | Posted on December 7th, 2015Carbon nanotubes grown in a furnace aren't always straight. Sometimes they curve and kink, and sometimes they branch off in several directions. The Rice researchers realized they now had the tools available to examine just how tough those branches are.
They used experiments and simulations to study the stiffness of joined nanotubes and found significant differences that are defined by their forms. It turned out that some types are tougher than others, and that all may have their uses if and when nanotubes are used to build macroscale structures.
The team led by Rice materials scientist Pulickel Ajayan and theoretical physicist Boris Yakobson named their nanotubes for their shapes: I for straight nanotubes, Y for branched, X for covalently joined tubes that cross, the lambda symbol (an upside-down "V") for nanotubes that join at any angle and the omega symbol (Ω) for noncovalent tubes that bind through van der Waals and other forces.
They said targeted synthesis of this "nanotube alphabet" may provide material for future nanoscale structures with tunable mechanisms.
The study was published by the American Chemical Society's Nano Letters.
"We needed some sort of language to describe the specific configuration of the junctions, so we thought, 'Let's use letters,'" said Evgeni Penev, a co-author and research scientist in Yakobson's group.
Chandra Sekhar Tiwary, a postdoctoral researcher in the Ajayan lab, prodded the nanotube junctions with a PicoIndenter that measures force and displacement in nanonewtons (billionths of a newton, a unit of force) and nanometers. The PicoIndenter was installed on a scanning electron microscope at Hysitron, a nanomechanical test-instrument manufacturing and testing company in Minneapolis.
Nanotubes grown by Rice graduate student Sehmus Ozden were dispersed in a solution, dried on silicon and placed under the microscope, where Tiwary scanned them for candidate "letters." He then had to be sure those candidates were single units and not just two separate nanotubes. "The space between the tubes could be as little as 1 nanometer but the resolution of the microscope was 5 nanometers, so we had to pick up one side (of the nanotubes) to be sure they were truly welded," he said. "If the nanotubes separated easily, we moved on to the next candidate."
Applying the probe to a particular spot on an individual nanotube was a test of patience, Tiwary said. Once a good candidate appeared, he and Hysitron senior staff scientist and co-author Sanjit Bhowmick zeroed in on the junction and, over 20 minutes, slowly applied and released enough pressure to compress it without breaking it. "In the old days, these tests used brute force, but the new tools are remarkable," Tiwary said. "We were able to watch as we compressed the nanotubes."
Among the atomically bonded tubes, they found the X's were the stiffest and most able to bounce back to nearly their original shapes. Next came Y's and then the any-angle lambdas, but all were left with dents because of newly created links between the inner walls. The I's and omegas, with no covalent bonds joining them to other nanotubes, returned to their original configurations.
The experimentalists turned to graduate student Yang Yang of Yakobson's theoretical group to help understand the mechanism by which the nanotubes handled stress. Yang created atom-level, triple-walled computer models of each "letter" and tested their strength with virtual probes.
"In experiments, we get what is happening quantitatively, but they cannot tell us what is happening inside the tubes," Tiwary said. "Until they did the calculations, we didn't really know how carbon nanotube junctions behaved."
The answer had to do with the atomic geometry at the junctions. Where nanotubes join, carbon atoms that normally come together in six-member rings are often forced to change their configurations, adjusting to five- and seven-member rings (known as dislocations) to remain in the lowest-energy state.
The number of dislocations required to make a nanotube branch is different for each angle. Because the dislocations take the brunt of the force, those variations determine the overall stiffness of the nanotube letter, they determined.
Previous research by Yakobson's group found that while graphene, the atom-thick, chicken-wire-like form of carbon, is extraordinarily strong, it does not stretch very well. But the new simulations also showed the local walls of the nanotubes (which are basically rolled-up graphene) stretch enough to distribute strain applied to the junctions.
Penev suggested that nanotube carpets of certain letters could have material benefits. "Imagine if all the nanotubes were upside-down 'Y' shapes," he said. "Such a carpet would be much harder to crush under pressure."
One question now is whether scientists can grow homogenous batches of letters. "Can we have all Y's and align them perfectly? Or can we have all X interconnects and then make a structure?" Tiwary asked. "That is going to be the next challenge, but it's just a matter of people putting time into it. I'm optimistic."
Syed Asif, director of research and development at Hysitron, is a co-author of the paper. Yakobson is the Karl F. Hasselmann Professor of Materials Science and NanoEngineering and a professor of chemistry. Ajayan is chair of Rice's Department of Materials Science and NanoEngineering, the Benjamin M. and Mary Greenwood Anderson Professor in Engineering and a professor of chemistry.
The research was supported by the U.S. Department of Defense Air Force Office of Scientific Research for the Project MURI: “Synthesis and Characterization of 3-D Carbon Nanotube Solid Networks." Computer resources were provided by XSEDE and Rice's DAVinCI cluster, both supported by the National Science Foundation.
####
About Rice University
Located on a 300-acre forested campus in Houston, Rice University is consistently ranked among the nation’s top 20 universities by U.S. News & World Report. Rice has highly respected schools of Architecture, Business, Continuing Studies, Engineering, Humanities, Music, Natural Sciences and Social Sciences and is home to the Baker Institute for Public Policy. With 3,888 undergraduates and 2,610 graduate students, Rice’s undergraduate student-to-faculty ratio is 6-to-1. Its residential college system builds close-knit communities and lifelong friendships, just one reason why Rice is ranked No. 1 for best quality of life and for lots of race/class interaction by the Princeton Review. Rice is also rated as a best value among private universities by Kiplinger’s Personal Finance.
Follow Rice News and Media Relations via Twitter @RiceUNews
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Jeff Falk
713-348-6327
Mike Williams
713-348-6728
Copyright © Rice University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() Rice Department of Materials Science and NanoEngineering:
Rice Department of Materials Science and NanoEngineering:
![]() George R. Brown School of Engineering:
George R. Brown School of Engineering:
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Videos/Movies
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() New X-ray imaging technique to study the transient phases of quantum materials December 29th, 2022
New X-ray imaging technique to study the transient phases of quantum materials December 29th, 2022
![]() Solvent study solves solar cell durability puzzle: Rice-led project could make perovskite cells ready for prime time September 23rd, 2022
Solvent study solves solar cell durability puzzle: Rice-led project could make perovskite cells ready for prime time September 23rd, 2022
![]() Scientists prepare for the world’s smallest race: Nanocar Race II March 18th, 2022
Scientists prepare for the world’s smallest race: Nanocar Race II March 18th, 2022
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Nanotubes/Buckyballs/Fullerenes/Nanorods/Nanostrings/Nanosheets
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








