Home > Press > Quantum computer made of standard semiconductor materials: Magnetic field helps qubit electrons store information longer
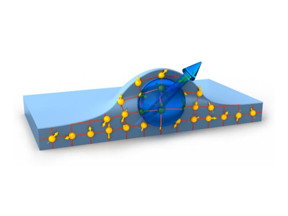 |
| By evaporating indium gallium arsenide onto a gallium arsenide substrate TUM physicists created nanometer-scale hills, so-called quantum dots. An electron trapped in one of these quantum dots can be used to store information. Hitherto unknown memory loss mechanisms could be switched off by applying a magnetic field. CREDIT: Fabian Flassig / TUM |
Abstract:
Physicists at the Technical University of Munich, the Los Alamos National Laboratory and Stanford University (USA) have tracked down semiconductor nanostructure mechanisms that can result in the loss of stored information - and halted the amnesia using an external magnetic field. The new nanostructures comprise common semiconductor materials compatible with standard manufacturing processes.
Quantum computer made of standard semiconductor materials: Magnetic field helps qubit electrons store information longer
Munich, Germany | Posted on December 3rd, 2015Quantum bits, qubits for short, are the basic logical elements of quantum information processing (QIP) that may represent the future of computer technology. Since they process problems in a quantum-mechanical manner, such quantum computers might one day solve complex problems much more quickly than currently possible, so the hope of researchers.
In principle, there are various possibilities of implementing qubits: photons are an option equally as viable as confined ions or atoms whose states can be altered in a targeted manner using lasers. The key questions regarding their potential use as memory units are how long information can be stored in the system and which mechanisms might lead to a loss of information.
A team of physicists headed by Alexander Bechtold and Professor Jonathan Finley at the Walter Schottky Institute of the Technical University of Munich and the Cluster of Excellence Nanosystems Initiative Munich (NIM) have now presented a system comprising a single electron trapped in a semiconductor nanostructure. Here, the electron's spin serves as the information carrier.
The researchers were able to precisely demonstrate the existence of different data loss mechanisms and also showed that stored information can nonetheless be retained using an external magnetic field.
Electrons trapped in a quantum dot
The TUM physicists evaporated indium gallium arsenide onto a gallium arsenide substrate to form their nanostructure. As a result of the different lattice spacing of the two semiconductor materials strain is produced at the interface between the crystal grids. The system thus forms nanometer-scale "hills" - so-called quantum dots.
When the quantum dots are cooled down to liquid helium temperatures and optically excited, a singe electron can be trapped in each of the quantum dots. The spin states of the electrons can then be used as information stores. Laser pulses can read and alter the states optically from outside. This makes the system ideal as a building block for future quantum computers.
Spin up or spin down correspond to the standard logical information units 0 and 1. But, on top of this come additional intermediate states of quantum mechanical up and down superpositions.
Hitherto unknown memory loss mechanisms
However, there is one problem: "We found out that the strain in the semiconductor material leads to a new and until recently unknown mechanism that results in the loss of quantum information," says Alexander Bechtold. The strain creates tiny electric fields in the semiconductor that influence the nuclear spin orientation of the atomic nuclei.
"It's a kind of piezoelectric effect," says Bechthold. "It results in uncontrolled fluctuations in the nuclear spins." These can, in turn, modify the spin of the electrons, i.e. the stored information. The information is lost within a few hundred nanoseconds.
In addition, Alexander Bechthold's team was able to provide concrete evidence for further information loss mechanisms, for example that electron spins are generally influenced by the spins of the surrounding 100,000 atomic nuclei.
Preventing quantum mechanical amnesia
"However, both loss channels can be switched off when a magnetic field of around 1.5 tesla is applied," says Bechtold. "This corresponds to the magnetic field strength of a strong permanent magnet. It stabilizes the nuclear spins and the encoded information remains intact."
"Overall, the system is extremely promising," according to Jonathan Finley, head of the research group. "The semiconductor quantum dots have the advantage that they harmonize perfectly with existing computer technology since they are made of similar semiconductor material." They could even be equipped with electrical contacts, allowing them to be controlled not only optically using a laser, but also using voltage pulses.
###
The research was funded by the European Union (S3 Nano and BaCaTeC), the US Department of Energy, the US Army Research Office (ARO), the German Research Foundation DFG (Cluster of Excellence Nanosystems Munich (NIM) and SFB 631), the Alexander von Humboldt Foundation as well as the TUM Institute for Advanced Study (Focus Group Nanophotonics and Quantum Optics).
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Andreas Battenberg
49-892-891-0510
Copyright © Technical University of Munich
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
Magnetism/Magnons
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Quantum Computing
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
Quantum Dots/Rods
![]() A new kind of magnetism November 17th, 2023
A new kind of magnetism November 17th, 2023
![]() IOP Publishing celebrates World Quantum Day with the announcement of a special quantum collection and the winners of two prestigious quantum awards April 14th, 2023
IOP Publishing celebrates World Quantum Day with the announcement of a special quantum collection and the winners of two prestigious quantum awards April 14th, 2023
![]() Qubits on strong stimulants: Researchers find ways to improve the storage time of quantum information in a spin rich material January 27th, 2023
Qubits on strong stimulants: Researchers find ways to improve the storage time of quantum information in a spin rich material January 27th, 2023
![]() NIST’s grid of quantum islands could reveal secrets for powerful technologies November 18th, 2022
NIST’s grid of quantum islands could reveal secrets for powerful technologies November 18th, 2022
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








