Home > Press > Rice makes light-driven nanosubmarines: Speedy single-molecule submersibles are a first
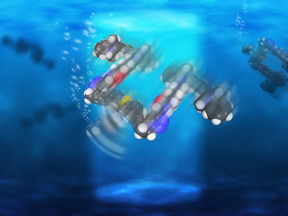 |
| Rice University scientists have created light-driven, single-molecule submersibles that contain just 244 atoms. Illustration by Loïc Samuel/Rice University |
Abstract:
Though they're not quite ready for boarding a lá "Fantastic Voyage," nanoscale submarines created at Rice University are proving themselves seaworthy.
Rice makes light-driven nanosubmarines: Speedy single-molecule submersibles are a first
Houston, TX | Posted on November 16th, 2015Each of the single-molecule, 244-atom submersibles built in the Rice lab of chemist James Tour has a motor powered by ultraviolet light. With each full revolution, the motor's tail-like propeller moves the sub forward 18 nanometers.
And with the motors running at more than a million RPM, that translates into speed. Though the sub's top speed amounts to less than 1 inch per second, Tour said that's a breakneck pace on the molecular scale.
"These are the fastest-moving molecules ever seen in solution," he said.
Expressed in a different way, the researchers reported this month in the American Chemical Society journal Nano Letters that their light-driven nanosubmersibles show an "enhancement in diffusion" of 26 percent. That means the subs diffuse, or spread out, much faster than they already do due to Brownian motion, the random way particles spread in a solution.
While they can't be steered yet, the study proves molecular motors are powerful enough to drive the sub-10-nanometer subs through solutions of moving molecules of about the same size.
"This is akin to a person walking across a basketball court with 1,000 people throwing basketballs at him," Tour said.
Tour's group has extensive experience with molecular machines. A decade ago, his lab introduced the world to nanocars, single-molecule cars with four wheels, axles and independent suspensions that could be "driven" across a surface.
Tour said many scientists have created microscopic machines with motors over the years, but most have either used or generated toxic chemicals. He said a motor that was conceived in the last decade by a group in the Netherlands proved suitable for Rice's submersibles, which were produced in a 20-step chemical synthesis.
"These motors are well-known and used for different things," said lead author and Rice graduate student Victor García-López. "But we were the first ones to propose they can be used to propel nanocars and now submersibles."
The motors, which operate more like a bacteria's flagellum than a propeller, complete each revolution in four steps. When excited by light, the double bond that holds the rotor to the body becomes a single bond, allowing it to rotate a quarter step. As the motor seeks to return to a lower energy state, it jumps adjacent atoms for another quarter turn. The process repeats as long as the light is on.
For comparison tests, the lab also made submersibles with no motors, slow motors and motors that paddle back and forth. All versions of the submersibles have pontoons that fluoresce red when excited by a laser, according to the researchers. (Yellow, sadly, was not an option.)
"One of the challenges was arming the motors with the appropriate fluorophores for tracking without altering the fast rotation," García-López said.
Once built, the team turned to Gufeng Wang at North Carolina State University to measure how well the nanosubs moved.
"We had used scanning tunneling microscopy and fluorescence microscopy to watch our cars drive, but that wouldn't work for the submersibles," Tour said. "They would drift out of focus pretty quickly."
The North Carolina team sandwiched a drop of diluted acetonitrile liquid containing a few nanosubs between two slides and used a custom confocal fluorescence microscope to hit it from opposite sides with both ultraviolet light (for the motor) and a red laser (for the pontoons).
The microscope's laser defined a column of light in the solution within which tracking occurred, García-López said. "That way, the NC State team could guarantee it was analyzing only one molecule at a time," he said.
Rice's researchers hope future nanosubs will be able to carry cargoes for medical and other purposes. "There's a path forward," García-López said. "This is the first step, and we've proven the concept. Now we need to explore opportunities and potential applications."
Co-authors of the paper are Rice alumnus Pinn-Tsong Chiang and postdoctoral researcher Gedeng Ruan; North Carolina State graduate student Fang Chen; Angel Martí, an associate professor of chemistry, of bioengineering and of materials science and nanoengineering, and Anatoly Kolomeisky, a professor of chemistry and of chemical and biomolecular engineering, both at Rice.
Wang is an assistant professor of analytical chemistry at North Carolina State. Tour is the T.T. and W.F. Chao Chair in Chemistry as well as a professor of computer science and of materials science and nanoengineering.
The National Science Foundation, the National Institutes of Health, the Welch Foundation and North Carolina State supported the research.
####
About Rice University
Located on a 300-acre forested campus in Houston, Rice University is consistently ranked among the nation’s top 20 universities by U.S. News & World Report. Rice has highly respected schools of Architecture, Business, Continuing Studies, Engineering, Humanities, Music, Natural Sciences and Social Sciences and is home to the Baker Institute for Public Policy. With 3,910 undergraduates and 2809 graduate students, Rice’s undergraduate student-to-faculty ratio is 6-to-1. Its residential college system builds close-knit communities and lifelong friendships, just one reason why Rice is ranked No. 1 for best quality of life and for lots of race/class interaction by the Princeton Review. Rice is also rated as a best value among private universities by Kiplinger’s Personal Finance.
Follow Rice News and Media Relations via Twitter @RiceUNews
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
David Ruth
713-348-6327
Mike Williams
713-348-6728
Copyright © Rice University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() Wiess School of Natural Sciences:
Wiess School of Natural Sciences:
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Molecular Machines
![]() First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
![]() Nanotech scientists create world's smallest origami bird March 17th, 2021
Nanotech scientists create world's smallest origami bird March 17th, 2021
![]() Giant nanomachine aids the immune system: Theoretical chemistry August 28th, 2020
Giant nanomachine aids the immune system: Theoretical chemistry August 28th, 2020
Molecular Nanotechnology
![]() Quantum pumping in molecular junctions August 16th, 2024
Quantum pumping in molecular junctions August 16th, 2024
![]() Scientists push the boundaries of manipulating light at the submicroscopic level March 3rd, 2023
Scientists push the boundaries of manipulating light at the submicroscopic level March 3rd, 2023
![]() First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








