Home > Press > New Oregon approach for 'nanohoops' could energize future devices: While application is down the road, these tiny organic circular structures could be used in solar cells, light-emitting diodes and medical diagnostics
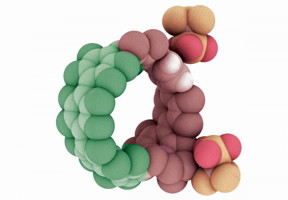 |
| Illustration of a cycloparaphenylene, or nanohoop, that has been doped with nitrogen atoms. Research in the University of Oregon lab of Ramesh Jasti has shown the combination of nitrogen and carbon atoms extends the potential efficiency and capabilities of such structures.
Courtesy of Ramesh Jasti |
Abstract:
When Ramesh Jasti began making tiny organic circular structures using carbon atoms, the idea was to improve carbon nanotubes being developed for use in electronics or optical devices. He quickly realized, however, that his technique might also roll solo.
New Oregon approach for 'nanohoops' could energize future devices: While application is down the road, these tiny organic circular structures could be used in solar cells, light-emitting diodes and medical diagnostics
Eugene, OR | Posted on October 12th, 2015In a new paper, Jasti and five University of Oregon colleagues show that his nanohoops -- known chemically as cycloparaphenylenes -- can be made using a variety of atoms, not just those from carbon. They envision these circular structures, which efficiently absorb and distribute energy, finding a place in solar cells, organic light-emitting diodes or as new sensors or probes for medicine.
The research, led by Jasti's doctoral student Evan R. Darzi, was described in a paper placed online ahead of print in ACS Central Science, a journal of the American Chemical Society. The paper is a proof-of-principle for the process, which will have to wait for additional research to be completed before the full impact of these new nanohoops can be realized, Jasti said.
These barely one-nanometer nanohoops offer a new class of structures -- sized between those made with long-chained polymers and small, low-weight molecules -- for use in energy or light devices, said Jasti, who was the first scientist to synthesize these types of molecules in 2008 as a postdoctoral fellow at the Molecular Foundry at the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory.
"These structures add to the toolbox and provide a new way to make organic electronic materials," Jasti said. "Cyclic compounds can behave like they are hundreds of units long, like polymers, but be only six to eight units around. We show that by adding non-carbon atoms, we are able to move the optical and electronic properties around."
Nanohoops help solve challenges related to materials with controllable band gaps -- the energies that lie between valance and conduction bands and is vital for designing organic semiconductors. Currently long materials such as those based on polymers work best.
"If you can control the band gap, then you can control the color of light that is emitted, for example," Jasti said. "In an electronic device, you also need to match the energy levels to the electrodes. In photovoltaics, the sunlight you want to capture has to match that gap to increase efficiency and enhance the ability to line up various components in optimal ways. These things all rely on the energy levels of the molecules. We found that the smaller we make nanohoops, the smaller the gap."
To prove their approach could work, Darzi synthesized a variety of nanohoops using both carbon and nitrogen atoms to explore their behavior. "What we show is that the charged nitrogen makes a nanohoop an acceptor of electrons, and the other part becomes a donator of electrons," Jasti said.
"The addition of other elements like nitrogen gives us another way to manipulate the energy levels, in addition to the nanohoop size. We've now shown that the nanohoop properties can be easily manipulated and, therefore, these molecules represent a new class of organic semiconductors -- similar to conductive polymers that won the Nobel Prize in 2000," he said. "With nanohoops, you can bind other things in the middle of the hoop, essentially doping them to change properties or perhaps sense an analyte that allows on-off switching."
His early work making nanohoop compounds was carbon-based, with the idea of making them different diameters and then combining them, but his group kept seeing unique and unexpected electronic and optical properties.
Jasti, winner of a National Science Foundation Career Award in 2013, brought his research from Boston University to the UO's Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry in 2014. He said the solar cell research being done by his colleagues in the Materials Science Institute, of which he is a member, was an important factor in his decision to move to the UO.
"We haven't gotten very far into the application of this," he said. "We're looking at that now. What we were able to see is that we can easily manipulate the energy levels of the structure, and now we know how to exchange any atom at any position along the loop. That is the key discovery, and it could be useful for all kinds of semiconductor applications."
###
Co-authors with Darzi and Jasti were: former BU doctoral student Elizabeth S. Hirst, who now is a postdoctoral fellow at the U.S. Army Natick Soldier Research, Development and Engineering Center; UO doctoral student Christopher D. Weber; Lev N. Zakharov, director of X-ray crystallography in the UO's Advanced Materials Characterization in Oregon center; and Mark C. Lonergan, a professor in the Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry.
The NSF (grant CHE-1255219), Department of Energy (DE-SC0012363), Sloan Foundation and Camille and Henry Dreyfus Foundation supported the research.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Jim Barlow
541-346-3481
Source:
Ramesh Jasti
associate professor
Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry
541-346-2508
Copyright © University of Oregon
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry:
Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry:
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Display technology/LEDs/SS Lighting/OLEDs
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Efficient and stable hybrid perovskite-organic light-emitting diodes with external quantum efficiency exceeding 40 per cent July 5th, 2024
Efficient and stable hybrid perovskite-organic light-emitting diodes with external quantum efficiency exceeding 40 per cent July 5th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Nanotubes/Buckyballs/Fullerenes/Nanorods/Nanostrings/Nanosheets
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
![]() Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








