Home > Press > Discovery about new battery overturns decades of false assumptions
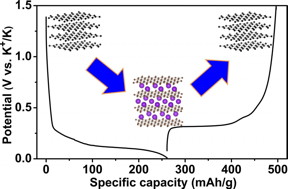 |
| This graphic outlines the electrical capacity of a newly developed potassium-ion battery. CREDIT: Graphic courtesy of Oregon State University |
Abstract:
New findings at Oregon State University have overturned a scientific dogma that stood for decades, by showing that potassium can work with graphite in a potassium-ion battery - a discovery that could pose a challenge and sustainable alternative to the widely-used lithium-ion battery.
Discovery about new battery overturns decades of false assumptions
Corvallis, OR | Posted on October 7th, 2015Lithium-ion batteries are ubiquitous in devices all over the world, ranging from cell phones to laptop computers and electric cars. But there may soon be a new type of battery based on materials that are far more abundant and less costly.
A potassium-ion battery has been shown to be possible. And the last time this possibility was explored was when Herbert Hoover was president, the Great Depression was in full swing and the Charles Lindbergh baby kidnapping was the big news story of the year - 1932.
"For decades, people have assumed that potassium couldn't work with graphite or other bulk carbon anodes in a battery," said Xiulei (David) Ji, the lead author of the study and an assistant professor of chemistry in the College of Science at Oregon State University.
"That assumption is incorrect," Ji said. "It's really shocking that no one ever reported on this issue for 83 years."
The Journal of the American Chemical Society published the findings from this discovery, which was supported by the U.S. Department of Energy and done in collaboration with OSU researchers Zelang Jian and Wei Luo. A patent is also pending on the new technology.
The findings are of considerable importance, researchers say, because they open some new alternatives to batteries that can work with well-established and inexpensive graphite as the anode, or high-energy reservoir of electrons. Lithium can do that, as the charge carrier whose ions migrate into the graphite and create an electrical current.
Aside from its ability to work well with a carbon anode, however, lithium is quite rare, found in only 0.0017 percent, by weight, of the Earth's crust. Because of that it's comparatively expensive, and it's difficult to recycle. Researchers have yet to duplicate its performance with less costly and more readily available materials, such as sodium, magnesium, or potassium.
"The cost-related problems with lithium are sufficient that you won't really gain much with economies of scale," Ji said. "With most products, as you make more of them, the cost goes down. With lithium the reverse may be true in the near future. So we have to find alternatives."
That alternative, he said, may be potassium, which is 880 times more abundant in the Earth's crust than lithium. The new findings show that it can work effectively with graphite or soft carbon in the anode of an electrochemical battery. Right now, batteries based on this approach don't have performance that equals those of lithium-ion batteries, but improvements in technology should narrow the gap, he said.
"It's safe to say that the energy density of a potassium-ion battery may never exceed that of lithium-ion batteries," he said. "But they may provide a long cycling life, a high power density, a lot lower cost, and be ready to take the advantage of the existing manufacturing processes of carbon anode materials."
Electrical energy storage in batteries is essential not only for consumer products such as cell phones and computers, but also in transportation, industry power backup, micro-grid storage, and for the wider use of renewable energy.
OSU officials say they are seeking support for further research and to help commercialize the new technology, through the OSU Office of Commercialization and Corporate Development.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Xiulei (David) Ji
541-737-6798
Copyright © Oregon State University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Automotive/Transportation
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Industrial
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() Quantum interference in molecule-surface collisions February 28th, 2025
Quantum interference in molecule-surface collisions February 28th, 2025
![]() Boron nitride nanotube fibers get real: Rice lab creates first heat-tolerant, stable fibers from wet-spinning process June 24th, 2022
Boron nitride nanotube fibers get real: Rice lab creates first heat-tolerant, stable fibers from wet-spinning process June 24th, 2022
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








