Home > Press > Nanoscale photodetector shows promise to improve the capacity of photonic circuits: Researchers at the University of Rochester have fabricated a device in which light can induce a current using a silver nanowire -- an important step toward harnessing light to speed up the next ge
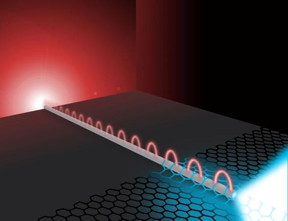 |
| This image shows light traveling along a silver nanowire as plasmons and re-emitted via molybdenum disulfide. CREDIT: M. Osadciw, University of Rochester, New York |
Abstract:
Photonic circuits, which use light to transmit signals, are markedly faster than electronic circuits. Unfortunately, they're also bigger. It's difficult to localize visible light below its diffraction limit, about 200-300 nanometers, and as components in electronic semiconductors have shrunk to the nanometer scale, the photonic circuit size limitation has given electronic circuits a significant advantage, despite the speed discrepancy.
Nanoscale photodetector shows promise to improve the capacity of photonic circuits: Researchers at the University of Rochester have fabricated a device in which light can induce a current using a silver nanowire -- an important step toward harnessing light to speed up the next ge
Washington, DC | Posted on October 6th, 2015Now researchers at the University of Rochester have demonstrated a key achievement in shrinking photonic devices below the diffraction limit -- a necessary step on the road to making photonic circuits competitive with today's technology. The scientists developed a nanoscale photodetector that uses the common material molybdenum disulfide to detect optical plasmons -- travelling oscillations of electrons below the diffraction limit -- and successfully demonstrated that light can drive a current using a silver nanowire.
"Our devices are a step towards miniaturization below the diffraction limit," said Kenneth Goodfellow, a graduate student in the laboratory of the Quantum Optoelectronics and Optical Metrology Group, The Institute of Optics, University of Rochester, New York. "It is a step towards using light to drive, or, at least complement electronic circuitry for faster information transfer."
The team will present their work at the Frontiers in Optics, The Optical Society's annual meeting and conference in San Jose, California, USA, on 22 October 2015.
The device expands on previous work demonstrating that light could be transmitted along a silver nanowire as a plasmon and re-emitted at the other end, which was covered with atomically-thin flakes of molybdenum disulfide (MoS2). When re-emitted, the light corresponded to the band gap of MoS2, rather than solely to the laser's wavelength, demonstrating that the plasmons effectively nudged the electrons in MoS2 into a different energy state.
"The natural next idea would be to see if this type of device would be able to be used as a photodetector," Goodfellow said.
To do this, the group transferred a silver nanowire coated at one end with MoS2 onto a silicon substrate and deposited metal contacts onto that same end with electron beam lithography. They then connected the device to equipment to control its bias, or fixed, voltage and to measure the current running through it.
When the uncovered end of the wire was exposed to a laser, the energy was converted into plasmons, a form of electromagnetic wave that travels through oscillations in electron density. This energy electronically excited an electron once it reached the molybdenum disulfide-covered end, effectively generating a current.
By scanning the wire bit-by-bit with a laser -- a process known as raster scanning -- the researchers were able to measure current at each point along the wire, finding that it was sensitive to the polarization of the incoming light and was at its strongest when the light was polarized parallel to the wire. They also found that the device was sensitive to the laser's excitation wavelength, and performance was limited at shorter wavelengths due to ineffective plasmon propagation and at longer wavelengths due to the band gap of molybdenum disulfide.
"Full photonic circuits are some time in the future, but this work helps to feed the current effort," Goodfellow said.
Future work for the group includes reducing potential contamination in device assembly by transitioning to a complete dry transfer of wires and MoS2 onto prefabricated electrodes, as well as gaining better control of the MoS2 doping process to add additional charge carriers and improve the device's efficiency.
###
About the Presentation
The presentation, "Detection of Optical Plasmons Using an Atomically-Thin Semiconductor," by Kenneth Goodfellow, will take place from 15:30 - 17:00, Thursday, 22 October 2015, in The Fairmont Hotel, San Jose, California, USA.
Media Registration: A media room for credentialed press and analysts will be located on-site in The Fairmont Hotel, 18-22 October 2015. Media interested in attending the event should register on the FiO website media center: Media Center.
####
About The Optical Society
Founded in 1916, The Optical Society (OSA) is the leading professional organization for scientists, engineers, students and entrepreneurs who fuel discoveries, shape real-life applications and accelerate achievements in the science of light. Through world-renowned publications, meetings and membership initiatives, OSA provides quality research, inspired interactions and dedicated resources for its extensive global network of optics and photonics experts. OSA is a founding partner of the National Photonics Initiative and the 2015 International Year of Light. For more information, visit: www.osa.org.
About FiO/LS
Frontiers in Optics (FiO) 2015 is The Optical Society's (OSA) 99th Annual Meeting and is being held with Laser Science, the 31th annual meeting of the American Physical Society (APS) Division of Laser Science (DLS). The two meetings unite the OSA and APS communities for five days of quality, cutting-edge presentations, in-demand invited speakers and a variety of special events spanning a broad range of topics in optics and photonics--the science of light--across the disciplines of physics, biology and chemistry. The exhibit floor will feature leading optics companies, technology products and programs. More information at: www.FrontiersinOptics.org.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Rebecca Andersen
202-416-1443
Research Contact:
Kenneth Goodfellow
University of Rochester
Rochester, NY
Copyright © The Optical Society
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Optical computing/Photonic computing
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
![]() Nanophotonic platform boosts efficiency of nonlinear-optical quantum teleportation April 25th, 2025
Nanophotonic platform boosts efficiency of nonlinear-optical quantum teleportation April 25th, 2025
![]() Groundbreaking research unveils unified theory for optical singularities in photonic microstructures December 13th, 2024
Groundbreaking research unveils unified theory for optical singularities in photonic microstructures December 13th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Events/Classes
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
![]() A New Blue: Mysterious origin of the ribbontail ray’s electric blue spots revealed July 5th, 2024
A New Blue: Mysterious origin of the ribbontail ray’s electric blue spots revealed July 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers demonstrate co-propagation of quantum and classical signals: Study shows that quantum encryption can be implemented in existing fiber networks January 20th, 2023
Researchers demonstrate co-propagation of quantum and classical signals: Study shows that quantum encryption can be implemented in existing fiber networks January 20th, 2023
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








