Home > Press > A necklace of fractional vortices
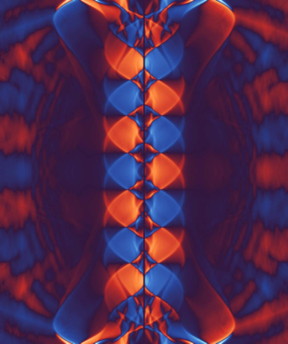 |
| A route to a time-reversal symmetry-broken state for d-wave superconductors is shown to occur via the formation of a necklace of fractional vortices around the perimeter of the material, where neighboring vortices have opposite current circulation. This vortex pattern is a result of a spectral rearrangement of current-carrying states near the edges. CREDIT: Mikael Håkansson |
Abstract:
Researchers at Chalmers University of Technology have arrived at how what is known as time-reversal symmetry can break in one class of superconducting material. The results have been published in the highly ranked Nature Physics journal, which also put the Chalmers researchers' study on the cover.
A necklace of fractional vortices
Gothenburg, Sweden | Posted on October 5th, 2015"Symmetries are an important aspect when describing nature", says Mikael Fogelström, who is a professor of theoretical physics at Chalmers University of Technology. "A ball is round and looks the same regardless of how we rotate it; thus, it has rotational symmetry. In the same way, most materials have symmetries that describe what the materials look like and what their properties are. If one or more symmetries breaks, this signals a phase transition to a new state. When a material becomes magnetic, a more abstract symmetry, what is known as time-reversal symmetry, is broken".
Superconducting materials conduct electric current without loss of energy. In 1986, researchers discovered that a family of perovskite materials - that have two-dimensional copper-oxide planes - becomes superconductive at relatively high temperatures. It could also thereafter be fairly quickly ascertained by experiments that the superconducting phase also broke the crystal symmetry, and that the material was unusual in this respect.
Theoreticians pondered whether the materials could also break time-reversal symmetry and produce spontaneous magnetisation. Experiments, primarily related to electron transport, showed that this was the case, while another category of experiments aimed at directly measuring the spontaneous magnetisation demonstrated no effect.
"Our work has arrived at a new mechanism for breaking time-reversal symmetry in high-temperature superconductors" says Tomas Löfwander, who is one of the researchers behind the new results. "We maintain that this has probably already been observed and that the two sets of experiments do not contradict one another."
The Chalmers researchers' discovery is based on a software package that researcher Mikael Håkansson developed while completing his licentiate thesis at the Division of Applied Quantum Physics at MC2, in order to produce a theoretical model of small mesoscopic superconducting grains. The software package utilises massive parallelisation of the numeric work, which can then be processed in graphics processing units, or GPUs.
"The time required to perform the fairly demanding computations was significantly reduced, and we were able to focus more on the physics and simulate more realistic systems", explains Mikael Håkansson. "At the same time, I developed a tool to process and visualise the large amounts of data that the software produced. The cover of the September issue of Nature Physics shows how the electron state is distributed in energy along a surface of a high-temperature superconductor when it has broken the time-reversal symmetry."
The computational tool has allowed the Chalmers researchers to investigate cases where the ring of a superconducting crystal affects the force of the superconducting phase. A periodic pattern of vortices spontaneously forms in the shape of a necklace along the surface as soon as the temperature is lower than a limit temperature. These vortices in turn cause a spontaneous magnetic flux that alternates direction on a length scale of a few dozen nanometers.
"We believe that new results with what are known as nanosquids, which are magnetometers with extremely good resolution, will be able to give immediate experimental verification of our results," says Mikael Fogelström.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Johanna Wilde
46-317-722-029
Copyright © Chalmers University of Technology
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Superconductivity
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








