Home > Press > Graphene as a front contact for silicon-perovskite tandem solar cells: HZB team develops elegant process for coating fragile perovskite layers with graphene for the first time
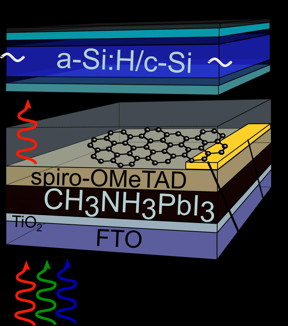 |
| The perovskite film (black, 200-300 nm) is covered by Spiro.OMeTAD, Graphene with gold contact at one edge, a glass substrate and an amorphous/crystalline silicon solar cell. CREDIT: F. Lang / HZB |
Abstract:
Teams at HZB have already acquired extensive experience with these kinds of tandem cells. A particularly effective complement to conventional silicon is the hybrid material called perovskite. It has a band gap of 1.6 electron volts with organic as well as inorganic components. However, it is very difficult to provide the perovskite layer with a transparent front contact. While sputter deposition of indium tin oxide (ITO) is common practice for inorganic silicon solar cells, this technique destroys the organic components of a perovskite cell.
Graphene as a front contact for silicon-perovskite tandem solar cells: HZB team develops elegant process for coating fragile perovskite layers with graphene for the first time
Berlin, Germany | Posted on October 5th, 2015Graphene as transparent front contact:
Now a group headed by Prof. Norbert Nickel has introduced a new solution. Dr. Marc Gluba and PhD student Felix Lang have developed a process to cover the perovskite layer evenly with graphene. Graphene consists of carbon atoms that have arranged themselves into a two-dimensional honeycomb lattice forming an extremely thin film that is highly conductive and highly transparent.
Fishing for graphene:
As a first step, the scientists promote growth of the graphene onto copper foil from a methane atmosphere at about 1000 degrees Celsius. For the subsequent steps, they stabilise the fragile layer with a polymer that protects the graphene from cracking. In the following step, Felix Lang etches away the copper foil. This enables him to transfer the protected graphene film onto the perovskite. "This is normally carried out in water. The graphene film floats on the surface and is fished out by the solar cell, so to speak. However, in this case this technique does not work, because the performance of the perovskite degrades with moisture. Therefore we had to find another liquid that does not attack perovskite, yet is as similar to water as possible", explains Gluba.
Ideal front contact:
Subsequent measurements showed that the graphene layer is an ideal front contact in several respects. Thanks to its high transparency, none of the sunlight's energy is lost in this layer. But the main advantage is that there are no open-circuit voltage losses, that are commonly observed for sputtered ITO layers. This increases the overall conversion efficiency. "This solution is comparatively simple and inexpensive to implement", says Nickel. "For the first time, we have succeeded in implementing graphene in a perovskite solar cell. This enabled us to build a high-efficiency tandem device."
###
Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters: Perovskite Solar Cells with Large-Area CVD-Graphene for Tandem Solar Cells; Felix Lang, Marc A. Gluba, Steve Albrecht, Jo?rg Rappich, Lars Korte, Bernd Rech, and Norbert H. Nickel
J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2015, 6 (14), pp 2745-2750
DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.5b0117
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Dr. Norbert Nickel
49-308-062-41301
Copyright © Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin für Materialien und Energie
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
![]() Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








