Home > Press > Extending a battery's lifetime with heat: Researchers from California Institute of Technology find that heat can break down the damaging branch-like structures that grow inside batteries, which may possibly be used to extend battery lifetimes
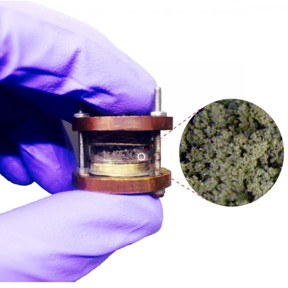 |
| This image shows naked-eye observation of amorphous/fractal lithium dendrites.
CREDIT: Asghar Aryanfar |
Abstract:
Don't go sticking your electronic devices in a toaster oven just yet, but for a longer-lasting battery, you might someday heat them up when not in use. Over time, the electrodes inside a rechargeable battery cell can grow tiny, branch-like filaments called dendrites, causing short circuits that kill the battery or even ignite it in flames. But thanks to new experiments and computer simulations, researchers from the California Institute of Technology have explored in detail how higher temperatures can break down these dendrites -- and possibly extend battery lifetimes.
Extending a battery's lifetime with heat: Researchers from California Institute of Technology find that heat can break down the damaging branch-like structures that grow inside batteries, which may possibly be used to extend battery lifetimes
Washington, DC | Posted on October 4th, 2015A battery cell consists of a positive and negative electrode, called the cathode and anode. As the battery produces electrical current, electrons flow from the anode through a circuit outside the battery and back into the cathode. Having lost the electrons that are generating the current, some of the atoms in the anode -- an electrically conductive metal like lithium -- become ions that then travel to the cathode, moving through a conductive liquid medium called an electrolyte.
Recharging the battery reverses the process, and the ions travel back and stick onto the anode. But when they do, the ions don't attach evenly. Instead, they form microscopic bumps that eventually grow into long branches after multiple recharging cycles. When these dendrites reach and contact the cathode, they form a short circuit. Electrical current now flows across the dendrites instead of the external circuit, rendering the battery useless and dead.
The current also heats up the dendrites, and because the electrolyte tends to be flammable, the dendrites can ignite. Even if the dendrites don't short circuit the battery, they can break off from the anode entirely and float around in the electrolyte. In this way, the anode loses material, and the battery can't store as much energy.
"Dendrites are hazardous and reduce the capacity of rechargeable batteries," said Asghar Aryanfar, a scientist at Caltech, who led the new study that's published this week on the cover of The Journal of Chemical Physics, from AIP Publishing. Although the researchers looked at lithium batteries, which are among the most efficient kind, their results can be applied broadly. "The dendrite problem is general to all rechargeable batteries," he said.
The researchers grew lithium dendrites on a test battery and heated them over a couple days. They found that temperatures up to 55 degrees Celsius shortened the dendrites by as much as 36 percent. To figure out what exactly caused this shrinkage, the researchers used a computer to simulate the effect of heat on the individual lithium atoms that comprise a dendrite, which was modeled with the simple, idealized geometry of a pyramid.
The simulations showed that increased temperatures triggered the atoms to move around in two ways. The atom at the tip of the pyramid can drop to lower levels. Or, an atom at a lower level can move and leave behind a vacant spot, which is then filled by another atom. The atoms shuffle around, generating enough motion to topple the dendrite.
By quantifying how much energy is needed to change the structure of the dendrite, Aryanfar said, researchers can better understand its structural characteristics. And while many factors affect a battery's longevity at high temperatures -- such as its tendency to discharge on its own or the occurrence of other chemical reactions on the side -- this new work shows that to revitalize a battery, all you might need is some extra heat.
The authors of this study are affiliated with the California Institute of Technology.
####
About American Institute of Physics
The Journal of Chemical Physics publishes concise and definitive reports of significant research in the methods and applications of chemical physics. See: jcp.aip.org
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Jason Socrates Bardi
240-535-4954
Copyright © American Institute of Physics
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








