Home > Press > Scientists found a natural nanostructure to control the flow of light
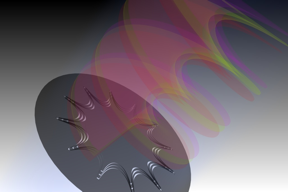 |
| An illustration of optical catenaries for the OAM generation. When a light beam incident on the catenary structures, orbital angular momenta are transferred from the structure to photons. This process is independent of the wavelength. Credit: SKLOTNM, Chinese Academy of Science |
Abstract:
Optical and photonic devices have become critical in current military and civil applications, such as laser weapons, remote sensing and infrared detection. Traditional optical devices are bulky and heavy because they rely on the phase accumulation on a long optical path. In an article published in Science Advances, a journal founded by the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS), Prof. Xiangang Luo from the Chinese Academy of Sciences and the co-workers have now demonstrated that ultrathin and lightweight optical devices could be constructed using nanostructures catenaries, which were typically used in architectures to construct incredible buildings. Two of the famous catenaries are the arches under the roof of Gaudí’s Casa Milà, Barcelona, Spain and the Gateway Arch in St. Louis, Missouri, United States.
Scientists found a natural nanostructure to control the flow of light
Shuangliu, China | Posted on October 4th, 2015The catenary is the curve that a free-hanging chain assumes under its own weight. It is a “true mathematical and mechanical form” in architecture described by Robert Hooke in the 1670s. The catenary could be found in many circumstances. For example, the silk on a spider's web form multiple elastic catenaries. The researchers now use optical catenary-shaped structures to convert circularly polarized light to helically-phased beam that carrying geometric linear phase profile. Similar to the “catenary of equal strength”, the phase gradient of the optical catenary is equal everywhere, which is a direct result of its special geometric shape. “The catenary structure could find applications in optics, architectures, and many other disciplines. This means that we could construct novel optical devices with strong similarity to the structures occurring in the natural world.” Prof. Luo explains.
Many previous methods used discrete nanostructures to generate space-variant phase distribution. The discrete structures lead to strong resonance, which makes the operating bandwidth of these samples limited. Prof. Luo’s group at the State Key Laboratory of Optical Technologies on Nano-fabrication and Micro-engineering (SKLOTNM), therefore uses the continuous catenary structures to obtain much broader bandwidth. They demonstrated that broadband orbital angular momentum (OAM) could be achieved by using the catenary array. The operating bandwidth of the devices could covers the entire electromagnetic spectrum ranging from microwave, terahertz, and infrared to the visible regime.
The catenaries could be used as a unique building block for optical metasurfaces, which are thought to be the key of the next-generation integrated optical systems. According to the metasurface-assisted law of reflection and refraction, many novel optical elements, such as flat lenses, axicons, and prisms, could be obtained with performance far beyond their traditional counterparts. Prof. Luo says, “The method of using catenary nanostructures to modulate phase works in many different circumstances. On the one hand, these nanostructures are natural candidates for the light manipulation on the nanoscale. On the other hand, when these structures are fabricated on flexible substrate, very lightweight and large-aperture lens could be realized. Such lenses make very large space telescopes become possible.”
Paper information:
M. Pu, X. Li, X. Ma, Y. Wang, Z. Zhao, C. Wang, C. Hu, P. Gao, C. Huang, H. Ren, X. Li, F. Qin, J. Yang, M. Gu, M. Hong, X. Luo, Catenary optics for achromatic generation of perfect optical angular momentum. Sci. Adv. 1, e1500396 (2015). DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.1500396
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Mingbo Pu
Copyright © Institute of Optics and Electronics, Chi
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
Aerospace/Space
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








