Home > Press > Quantum states in a nano-object manipulated using a mechanical system
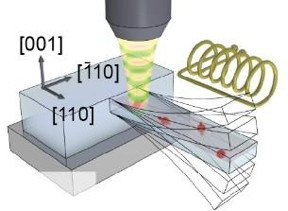 |
| The oscillating resonator influences the electron spin in the nitrogen-vacancy centers (red arrows). Their spin can be efficiently read out by fluorescence microscopy. CREDIT: University of Basel |
Abstract:
Scientists at the Swiss Nanoscience Institute at the University of Basel have used resonators made from single-crystalline diamonds to develop a novel device in which a quantum system is integrated into a mechanical oscillating system. For the first time, the researchers were able to show that this mechanical system can be used to coherently manipulate an electron spin embedded in the resonator - without external antennas or complex microelectronic structures. The results of this experimental study will be published in Nature Physics.
Quantum states in a nano-object manipulated using a mechanical system
Basel, Switzerland | Posted on August 3rd, 2015In previous publications, the research team led by Georg H. Endress Professor Patrick Maletinsky described how resonators made from single-crystalline diamonds with individually embedded electrons are highly suited to addressing the spin of these electrons. These diamond resonators were modified in multiple instances so that a carbon atom from the diamond lattice was replaced with a nitrogen atom in their crystal lattices with a missing atom directly adjacent. In these "nitrogen-vacancy centers," individual electrons are trapped. Their "spin" or intrinsic angular momentum is examined in this research.
When the resonator now begins to oscillate, strain develops in the diamond's crystal structure. This, in turn, influences the spin of the electrons, which can indicate two possible directions ("up" or "down") when measured. The direction of the spin can be detected with the aid of fluorescence spectroscopy.
Extremely fast spin oscillation
In this latest publication, the scientists have shaken the resonators in a way that allows them to induce a coherent oscillation of the coupled spin for the first time. This means that the spin of the electrons switches from up to down and vice versa in a controlled and rapid rhythm and that the scientists can control the spin status at any time. This spin oscillation is fast compared with the frequency of the resonator. It also protects the spin against harmful decoherence mechanisms.
It is conceivable that this diamond resonator could be applied to sensors - potentially in a highly sensitive way - because the oscillation of the resonator can be recorded via the altered spin. These new findings also allow the spin to be coherently rotated over a very long period of close to 100 microseconds, making the measurement more precise. Nitrogen-vacancy centers could potentially also be used to develop a quantum computer. In this case, the quick manipulation of its quantum states demonstrated in this work would be a decisive advantage.
###
Original source
Arne Barfuss, Jean Teissier, Elke Neu, Andreas Nunnenkamp, Patrick Maletinsky
Strong mechanical driving of a single electron spin
Nature Physics (2015), doi: 10.1038/nphys3411
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Olivia Poisson
Copyright © University of Basel
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
NEMS
![]() IEDM - CEA-Leti Will Present 11 Papers and Host Workshop on Disruptive Technologies for Data Management November 7th, 2018
IEDM - CEA-Leti Will Present 11 Papers and Host Workshop on Disruptive Technologies for Data Management November 7th, 2018
![]() UT engineers develop first method for controlling nanomotors: Breakthrough for nanotechnology as UT engineers develop first method for switching the mechanical motion of nanomotors September 21st, 2018
UT engineers develop first method for controlling nanomotors: Breakthrough for nanotechnology as UT engineers develop first method for switching the mechanical motion of nanomotors September 21st, 2018
![]() Nano-kirigami: 'Paper-cut' provides model for 3D intelligent nanofabrication July 13th, 2018
Nano-kirigami: 'Paper-cut' provides model for 3D intelligent nanofabrication July 13th, 2018
![]() One string to rule them all April 17th, 2018
One string to rule them all April 17th, 2018
Quantum Computing
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Quantum nanoscience
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








