Home > Press > Engineered hybrid crystal opens new frontiers for high-efficiency lighting: University of Toronto researchers successfully combine 2 different materials to create new hyper-efficient light-emitting crystal
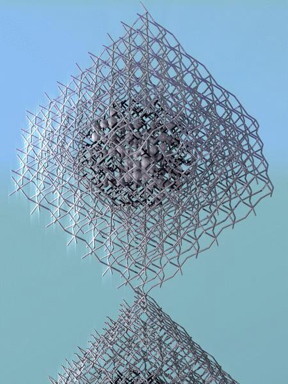 |
| A glowing quantum dot seamlessly integrated into a perovskite crystal matrix.
CREDIT: Sargent Group/ U of T Engineering |
Abstract:
It's snack time: you have a plain oatmeal cookie, and a pile of chocolate chips. Both are delicious on their own, but if you can find a way to combine them smoothly, you get the best of both worlds.
Engineered hybrid crystal opens new frontiers for high-efficiency lighting: University of Toronto researchers successfully combine 2 different materials to create new hyper-efficient light-emitting crystal
Toronto, Canada | Posted on July 16th, 2015Researchers in The Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering used this insight to invent something totally new: they've combined two promising solar cell materials together for the first time, creating a new platform for LED technology.
The team designed a way to embed strongly luminescent nanoparticles called colloidal quantum dots (the chocolate chips) into perovskite (the oatmeal cookie). Perovskites are a family of materials that can be easily manufactured from solution, and that allow electrons to move swiftly through them with minimal loss or capture by defects.
The work is published in the international journal Nature on July 15, 2015.
"It's a pretty novel idea to blend together these two optoelectronic materials, both of which are gaining a lot of traction," says Xiwen Gong, one of the study's lead authors and a PhD candidate working with Professor Ted Sargent. "We wanted to take advantage of the benefits of both by combining them seamlessly in a solid-state matrix."
The result is a black crystal that relies on the perovskite matrix to 'funnel' electrons into the quantum dots, which are extremely efficient at converting electricity to light. Hyper-efficient LED technologies could enable applications from the visible-light LED bulbs in every home, to new displays, to gesture recognition using near-infrared wavelengths.
"When you try to jam two different crystals together, they often form separate phases without blending smoothly into each other," says Dr. Riccardo Comin, a post-doctoral fellow in the Sargent Group. "We had to design a new strategy to = convince these two components to forget about their differences and to rather intermix into forming a unique crystalline entity."
The main challenge was making the orientation of the two crystal structures line up, called heteroexpitaxy. To achieve heteroepitaxy, Gong, Comin and their team engineered a way to connect the atomic 'ends' of the two crystalline structures so that they aligned smoothly, without defects forming at the seams. "We started by building a nano-scale scaffolding 'shell' around the quantum dots in solution, then grew the perovskite crystal around that shell so the two faces aligned," explained coauthor Dr. Zhijun Ning, who contributed to the work while a post-doctoral fellow at UofT and is now a faculty member at ShanghaiTech.
The resulting heterogeneous material is the basis for a new family of highly energy-efficient near-infrared LEDs. Infrared LEDs can be harnessed for improved night-vision technology, to better biomedical imaging, to high-speed telecommunications.
Combining the two materials in this way also solves the problem of self-absorption, which occurs when a substance partly re-absorbs the same spectrum of energy that it emits, with a net efficiency loss. "These dots in perovskite don't suffer reabsorption, because the emission of the dots doesn't overlap with the absorption spectrum of the perovskite," explains Comin.
Gong, Comin and the team deliberately designed their material to be compatible with solution-processing, so it could be readily integrated with the most inexpensive and commercially practical ways of manufacturing solar film and devices. Their next step is to build and test the hardware to capitalize on the concept they have proven with this work.
"We're going to build the LED device and try to beat the record power efficiency reported in the literature," says Gong.
###
This work was supported by the Ontario Research Fund Research Excellence Program, the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC), and the King Abdullah University of Science & Technology (KAUST).
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Marit Mitchell
416-978-7997
Copyright © University of Toronto Engineering
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Display technology/LEDs/SS Lighting/OLEDs
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Efficient and stable hybrid perovskite-organic light-emitting diodes with external quantum efficiency exceeding 40 per cent July 5th, 2024
Efficient and stable hybrid perovskite-organic light-emitting diodes with external quantum efficiency exceeding 40 per cent July 5th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Quantum Dots/Rods
![]() A new kind of magnetism November 17th, 2023
A new kind of magnetism November 17th, 2023
![]() IOP Publishing celebrates World Quantum Day with the announcement of a special quantum collection and the winners of two prestigious quantum awards April 14th, 2023
IOP Publishing celebrates World Quantum Day with the announcement of a special quantum collection and the winners of two prestigious quantum awards April 14th, 2023
![]() Qubits on strong stimulants: Researchers find ways to improve the storage time of quantum information in a spin rich material January 27th, 2023
Qubits on strong stimulants: Researchers find ways to improve the storage time of quantum information in a spin rich material January 27th, 2023
![]() NISTís grid of quantum islands could reveal secrets for powerful technologies November 18th, 2022
NISTís grid of quantum islands could reveal secrets for powerful technologies November 18th, 2022
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
![]() Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








