Home > Press > Spintronics advance brings wafer-scale quantum devices closer to reality
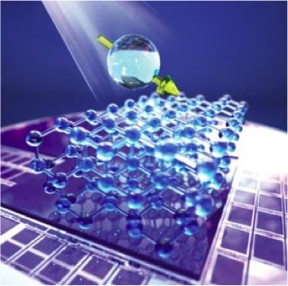 |
| Light polarizes silicon nuclear spins within a silicon carbide chip. This image portrays the nuclear spin of one of the atoms shown in the full crystal lattice below. CREDIT: Courtesy of Peter Allen |
Abstract:
An electronics technology that uses the "spin" - or magnetization - of atomic nuclei to store and process information promises huge gains in performance over today's electron-based devices. But getting there is proving challenging.
Spintronics advance brings wafer-scale quantum devices closer to reality
Chicago, IL | Posted on June 24th, 2015Now researchers at the University of Chicago's Institute for Molecular Engineering (IME) have made a crucial step toward nuclear spintronic technologies. They have gotten nuclear spins to line themselves up in a consistent, controllable way, and they have done it using a high-performance material that is practical, convenient, and inexpensive.
"Our results could lead to new technologies like ultra-sensitive magnetic resonance imaging, nuclear gyroscopes, and even computers that harness quantum mechanical effects," said Abram Falk, the lead author of the report on the research, which was featured as the cover article of the June 17 issue of Physical Review Letters. Falk and colleagues in David Awschalom's IME research group invented a new technique that uses infrared light to align spins. And they did so using silicon carbide (SiC), an industrially important semiconductor.
Nuclear spins tend to be randomly oriented. Aligning them in a controllable fashion is usually a complicated and only marginally successful proposition. The reason, explains Paul Klimov, a co-author of the paper, is that "the magnetic moment of each nucleus is tiny, roughly 1,000 times smaller than that of an electron."
This small magnetic moment means that little thermal kicks from surrounding atoms or electrons can easily randomize the direction of the nuclear spins. Extreme experimental conditions such as high magnetic fields and cryogenic temperatures (-238 degrees Fahrenehit and below) are usually required to get even a small number of spins to line up. In magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), for example, only one to 10 out of a million nuclear spins can be aligned and seen in the image, even with a high magnetic field applied.
Using their new technique, Awschalom and his associates aligned more than 99 percent of spins in certain nuclei in silicon carbide (SiC). Equally important, the technique works at room temperature -- no cryogenics or intense magnetic fields needed. Instead, the research team used light to "cool" the nuclei.
While nuclei do not themselves interact with light, certain imperfections, or "color-centers," in the SiC crystals do. The electron spins in these color centers can be readily optically cooled and aligned, and this alignment can be transferred to nearby nuclei. Had the group tried to achieve the same degree of spin alignment without optical cooling they would have had to chill the SiC chip physically to just five millionths of a degree above absolute zero (-459.6 degrees Fahrenheit).
Getting spins to align in room-temperature silicon carbide brings practical spintronic devices a significant step closer, said Awschalom, the Liew Family Professor in Spintronics and Quantum Information. The material is already an important semiconductor in the high-power electronics and opto-electronics industries. Sophisticated growth and processing capabilities are already mature. So prototypes of nuclear spintronic devices that exploit the IME researchers' technique may be developed in the near future. Said Awschalom: "Wafer-scale quantum technologies that harness nuclear spins as subatomic elements may appear more quickly than we anticipated." --Carla Reiter
###
Citation: "Optical Polarization of Nuclear Spins in Silicon Carbine," by Abram L. Falk, Paul V. Klimov, Viktor Ivády, Krisztián Szász, David J. Christle, William F. Koehl, Ádám Gali, and David D. Awschalom, Physical Review Letters, 114, 247603 (2015), DOI: 10.1103. Published June 17, 2015.
Funding and support: Air Force Office of Scientific Research, National Science Foundation, Knut & Alice Wallenberg Foundation, Hungarian Academy of Sciences, and Sweden's National Supercomputer Center.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Steve Koppes
773-702-8366
Copyright © University of Chicago
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Spintronics
![]() Quantum materials: Electron spin measured for the first time June 9th, 2023
Quantum materials: Electron spin measured for the first time June 9th, 2023
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Quantum Computing
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








