Home > Press > Basel physicists develop efficient method of signal transmission from nanocomponents
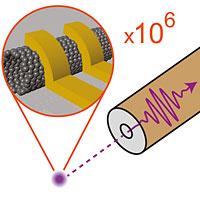 |
| The clever arrangement of two electrical conductors around the carbon nanotube leads to an efficient signal transmission between the carbon nanotube and a much larger conductor for electromagnetic waves. CREDIT:© University of Basel, Department of Physics/Swiss Nanoscience Institute |
Abstract:
Physicists have developed an innovative method that could enable the efficient use of nanocomponents in electronic circuits. To achieve this, they have developed a layout in which a nanocomponent is connected to two electrical conductors, which uncouple the electrical signal in a highly efficient manner. The scientists at the Department of Physics and the Swiss Nanoscience Institute at the University of Basel have published their results in the scientific journal Nature Communications together with their colleagues from ETH Zurich.
Basel physicists develop efficient method of signal transmission from nanocomponents
Basel, Switzerland | Posted on May 23rd, 2015Electronic components are becoming smaller and smaller. Components measuring just a few nanometers - the size of around ten atoms - are already being produced in research laboratories. Thanks to miniaturization, numerous electronic components can be placed in restricted spaces, which will boost the performance of electronics even further in the future.
Teams of scientists around the world are investigating how to produce such nanocomponents with the aid of carbon nanotubes. These tubes have unique properties - they offer excellent heat conduction, can withstand strong currents, and are suitable for use as conductors or semiconductors. However, signal transmission between a carbon nanotube and a significantly larger electrical conductor remains problematic as large portions of the electrical signal are lost due to the reflection of part of the signal.
Antireflex increases efficiency
A similar problem occurs with light sources inside a glass object. A large amount of light is reflected by the walls, which means that only a small proportion reaches the outside. This can be countered by using an antireflex coating on the walls.
Led by Professor Christian Schönenberger, scientists in Basel are now taking a similar approach to nanoelectronics. They have developed an antireflex device for electrical signals to reduce the reflection that occurs during transmission from nanocomponents to larger circuits. To do so, they created a special formation of electrical conductors of a certain length, which are coupled with a carbon nanotube. The researchers were therefore able to efficiently uncouple a high-frequency signal from the nanocomponent.
Differences in impedance cause the problem
Coupling nanostructures with significantly larger conductors proved difficult because they have very different impedances. The greater the difference in impedance between two conducting structures, the greater the loss during transmission. The difference between nanocomponents and macroscopic conductors is so great that no signal will be transmitted unless countermeasures are taken. The antireflex device minimizes this effect and adjusts the impedances, leading to efficient coupling. This brings the scientists significantly closer to their goal of using nanocomponents to transmit signals in electronic parts.
###
Original source
V. Ranjan, G. Puebla-Hellmann, M. Jung, T. Hasler, A. Nunnenkamp, M. Muoth, C. Hierold, A. Wallraff & C. Schönenberger
Clean carbon nanotubes coupled to superconducting impedance-matching circuits
Nature Communications (2015), doi: 10.1038/ncomms8165
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Olivia Poisson
Copyright © University of Basel
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Nanotubes/Buckyballs/Fullerenes/Nanorods/Nanostrings/Nanosheets
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Nanoelectronics
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
![]() Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
![]() Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








