Home > Press > Electron spin brings order to high entropy alloys
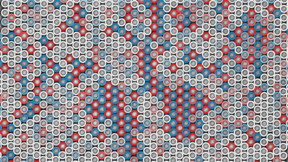 |
| This is a scanning transmission microscopy image with intensity ratios highlighted. The ordered nano domains have columns with higher intensity (red) residing next to columns of lower intensity (blue). CREDIT: Doug Irving and James LeBeau, North Carolina State University |
Abstract:
Researchers from North Carolina State University have discovered that electron spin brings a previously unknown degree of order to the high entropy alloy nickel iron chromium cobalt (NiFeCrCo) - and may play a role in giving the alloy its desirable properties.
Electron spin brings order to high entropy alloys
Raleigh, NC | Posted on April 23rd, 2015"High entropy alloys have garnered a lot of attention over the past 10 years because they have remarkable properties," says Doug Irving, an associate professor of materials science and engineering at NC State and corresponding author of a paper describing the work. High entropy alloys are materials that consist of four or more metals in approximately equal amounts.
"For example, NiFeCrCo-based high entropy alloys have a good combination of hardness, tensile strength, ductility, and fracture resistance at extremely low temperatures," Irving says.
"If you look at NiFeCrCo, it has a fixed structure," Irving explains. "Think of orderly rows of boxes. But which atoms fill which spaces is seemingly random - it seems impossible to predict which element might be might be in any given box. That impression of chaos is why they're called high entropy alloys.
"But now we have determined that there is some order in the composition of this alloy," Irving says.
Specifically, the researchers learned that chromium - and spin - play key roles.
All atoms have electrons, and all electrons have a property called spin. The electrons in ferromagnetic materials - like iron, nickel and cobalt - tend to align so that their spin is oriented in the same direction. But the electrons in antiferromagnetic materials - like chromium - tend to align so that their spin is the opposite of their neighbors.
In NiFeCrCo, chromium can align its spin against its neighbors if it is surrounded by iron, nickel or cobalt. They can all spin up, and chromium can spin down. But if two chromium atoms are next to each other they can't both align their spins differently from all of their neighbors - because they themselves are neighbors.
In short, chromium's spin properties force the chromium atoms to be as far apart as possible in the NiFeCrCo structure. And, because there is a high concentration of chromium atoms in the material, this creates nanoscale domains of order with the overall "chaos" of the high entropy alloy.
"Showing that this material has order at the nanoscale will likely lead to new work on how to expand these ordered domains, and potentially manipulate the material's mechanical properties," Irving says.
The researchers used a combination of advanced electronic structure calculations, magnetic property measurements, and revolving scanning transmission electron microscopy (revolving STEM) to see what was happening at the atomic scale in NiFeCrCo.
"It's a powerful example of what can be learned through combining state of the art microscopy techniques with predictions from advanced computational approaches," says James LeBeau, an assistant professor of materials science and engineering at NC State, co-author of the paper, and the creator of the revolving STEM technique.
###
The paper, "Spin-driven Ordering of Cr in the Equiatomic High Entropy Alloy NiFeCrCo," is published online in the journal Applied Physics Letters. Lead author of the paper is Changning Niu, a Ph.D. student at NC State. Co-authors include Alexander Zaddach, Adedapo Oni, Xiahan Sang, and Carl Koch of NC State; and James Hurt III of Furman University. The work was supported by the National Science Foundation under grants DMR-1104930 and EEC-1156762, and by the Air Force Office of Scientific Research under grant number FA9550-12-1-0456.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Matt Shipman
919-515-6386
Copyright © North Carolina State University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








