Home > Press > How many gold atoms make gold metal?
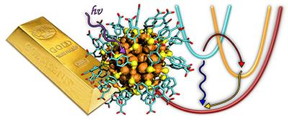 |
| Nanogold is different from macroscopic gold. The small 102-gold atom cluster (right) behaves like a giant molecule, but slightly larger 144-gold atom cluster is like a metal. The image on the right is from ref. 1 CREDIT: The University of Jyväskylä |
Abstract:
Researchers at the Nanoscience Center at the University of Jyväskylä, Finland, have shown that dramatic changes in the electronic properties of nanometre-sized chunks of gold occur in well-defined size range. Small gold nanoclusters could be used, for instance, in short-term storage of energy or electric charge in the field of molecular electronics. Funded by the Academy of Finland, the researchers have been able to obtain new information which is important, among other things, in developing bioimaging and sensing based on metal-like clusters.
How many gold atoms make gold metal?
Helsinki, Finland | Posted on April 11th, 2015Two recent papers by the researchers at Jyväskylä (1, 2) demonstrate that the electronic properties of two different but still quite similar gold nanoclusters can be drastically different. The clusters were synthesised by chemical methods incorporating a stabilising ligand layer on their surface. The researchers found that the smaller cluster, with up to 102 gold atoms, behaves like a giant molecule while the larger one, with at least 144 gold atoms, already behaves, in principle, like a macroscopic chunk of metal, but in nanosize.
The fundamentally different behaviour of these two differently sized gold nanoclusters was demonstrated by shining a laser light onto solution samples containing the clusters and by monitoring how energy dissipates from the clusters into the surrounding solvent.
"Molecules behave drastically different from metals," said Professor Mika Pettersson, the principal investigator of the team conducting the experiments. "The additional energy from light, absorbed by the metal-like clusters, transfers to the environment extremely rapidly, in about one hundred billionth of a second, while a molecule-like cluster is excited to a higher energy state and dissipates the energy into the environment with a rate that is at least 100 times slower. This is exactly what we saw: the 102-gold atom cluster is a giant molecule showing even a transient magnetic state while the 144-gold atom cluster is already a metal. We've thus managed to bracket an important size region where this fundamentally interesting change in the behaviour takes place."
"These experimental results go together very well with what our team has seen from computational simulations on these systems," said Professor Hannu Häkkinen, a co-author of the studies and the scientific director of the nanoscience centre. "My team predicted this kind of behaviour back in 2008-2009 when we saw big differences in the electronic structure of exactly these nanoclusters. It's wonderful that robust spectroscopic experiments have now proved these phenomena. In fact, the metal-like 144-atom cluster is even more interesting, since we just published a theoretical paper where we saw a big enhancement of the metallic properties of just a few copper atoms mixed with gold." (3)
###
The computational work was done at the CSC - the IT Center for Science in Espoo, Finland, and at the HLRS centre in Stuttgart, Germany.
References
1. S. Mustalahti, P. Myllyperkiö, S. Malola, T. Lahtinen, K. Salorinne, J. Koivisto, H. Häkkinen and M. Pettersson, "Molecule-Like Photodynamics of Au102(pMBA)44 Nanocluster", ACS Nano 9, 2328 (2015). DOI: 10.1021/nn506711a
2. S. Mustalahti, P. Myllyperkiö, T. Lahtinen, K. Salorinne, S. Malola, J. Koivisto, H. Häkkinen and M. Pettersson, "Ultrafast Electronic Relaxation and Vibrational Cooling Dynamics of Au144(SC2H4Ph)60 Nanocluster Probed by Transient Mid-IR Spectroscopy", J. Phys. Chem. C 118, 18233 (2014). DOI: 10.1021/jp505464z
3. S. Malola, M.Hartman and H. Häkkinen, "Copper Induces a Core Plasmon in Intermetallic Au(144,145)-xCux(SR)60 Nanoclusters", J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 6, 515 (2015). DOI: 10.1021/jz502637b
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Hannu Häkkinen
358-400-247-973
Professor Mika Pettersson
+358 50 310 9969
Leena Vähäkylä
Communications Specialist
Academy of Finland
tel. +358 295 335 139 or +358 40 359 2936
Copyright © Academy of Finland
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








