Home > Press > A qubit candidate shines brighter: Precisely placing imperfections called 'nitrogen vacancy centers' within nano-sized diamond structures can boost their fluorescence, a key step toward using the defects in future quantum computers
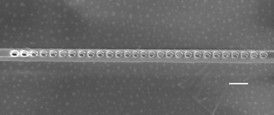 |
| A SCANNING ELECTRON MICROSCOPE IMAGE OF THE DIAMOND PHOTONIC CAVITY SHOWS THE NANOSCALE HOLES ETCHED THROUGH THE LAYER CONTAINING NV CENTERS. THE SCALE BAR INDICATES 200 NANOMETERS.
CREDIT: EVELYN HU/HARVARD |
Abstract:
In the race to design the world's first universal quantum computer, a special kind of diamond defect called a nitrogen vacancy (NV) center is playing a big role. NV centers consist of a nitrogen atom and a vacant site that together replace two adjacent carbon atoms in diamond crystal. The defects can record or store quantum information and transmit it in the form of light, but the weak signal is hard to identify, extract and transmit unless it is intensified.
A qubit candidate shines brighter: Precisely placing imperfections called 'nitrogen vacancy centers' within nano-sized diamond structures can boost their fluorescence, a key step toward using the defects in future quantum computers
Washington, DC | Posted on December 29th, 2014Now a team of researchers at Harvard, the University of California, Santa Barbara and the University of Chicago has taken a major step forward in effectively enhancing the fluorescent light emission of diamond nitrogen vacancy centers - a key step to using the atom-sized defects in future quantum computers. The technique, described in the journal Applied Physics Letters, from AIP Publishing, hinges on the very precise positioning of NV centers within a structure called a photonic cavity that can boost the light signal from the defect.
A Potential Qubit Power Couple
NV centers contain an unpaired electron that can store information in a property known as spin. Researchers can "read" the spin state of the electron by observing the intensity of particular frequencies of the light that the NV center emits when illuminated by a laser.
At room temperatures, this pattern of light emission couples to multiple "sideband" frequencies, making it difficult to interpret. To amplify the most important element of the signal researchers can use a structure called a photonic cavity, which consists of a pattern of nanoscale holes that serve to enhance the NV center's light emission at its main frequency.
"A photonic cavity that is properly matched to the NVs can substantially augment their capabilities," said Evelyn Hu, a researcher at Harvard whose group studies the optical and electronic behavior of materials that have been carefully sculpted at the nanoscale.
NV centers whose signal is enhanced by photonic cavities could act as qubits, the fundamental units of quantum information in a quantum computer.
Matchmaker, Matchmaker, Make Me a Match
Photonic cavities best enhance the signal of NV centers located in a "hot spot" where the cavities' resonant fields are strongest, but making sure an atom-sized defect's location matches up with this spot is extremely tricky.
"Strong spatial overlap is the hardest [task] to achieve in designing and fabricating a photonic cavity for NV centers," Hu said.
She compared the task to turning on a fixed small light beam in a dark room containing ultra-small transmitters that send out information once they are illuminated by the 'right' beam. If the match is right, the signal from the transmitter is returned strongly, but the challenge is that the chances of the light hitting the transmitter are very small.
Hu and her colleagues ultimately aim to make sure the beam (or field of the photonic cavity) will always hit the transmitter (or NV center), so that information will always be read out. They can do this by knowing the exact position of the tiny NV centers.
The team took an important first step toward this goal by controlling the depth of the diamond defects using a technique called delta doping. "Integrating a plane of spins into these structures enables us to engineering the spin-photon interaction and exploit quantum effects for future technologies," said David Awschalom, a researcher at the University of Chicago whose group grows and characterizes these systems. The technique confines the possible location of NV centers to a layer approximately 6 nanometers thick sandwiched inside a diamond membrane approximately 200 nanometers thick. The researchers then etched holes into the membrane to create the photonic cavities.
Using this method the researchers were able to increase the intensity of the light emitted by the NV centers by a factor of about 30 times.
The team believes they can further enhance the emission by also controlling the position of the defects in the horizontal plane and are currently working on possible ways to achieve full 3-D control.
Computers, Sensors and More
Nitrogen vacancy centers aren't the only candidate for qubits, but they have attracted a lot of interest because their electrons have long spin lifetimes at room temperature, meaning they can maintain quantum information for a relatively long time.
And the promise of NV centers doesn't stop at ultrafast computers. NV centers can also be used in non-computing applications, for examples as molecular-scale magnetic and temperature sensors that could measure the properties within single cells.
####
About Applied Physics Letters
Applied Physics Letters features concise, rapid reports on significant new findings in applied physics. The journal covers new experimental and theoretical research on applications of physics phenomena related to all branches of science, engineering, and modern technology.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Jason Socrates Bardi
240-535-4954
Copyright © Applied Physics Letters
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Quantum Computing
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








