Home > Press > Pseudospin-driven spin relaxation mechanism in graphene
 |
Abstract:
Members of ICN2 Theoretical and Computational Nanoscience Group unveil an unprecedented spin relaxation mechanism unique to graphene, and related with entanglement of spin and pseudospin quantum degrees of freedom in presence of weak spin-orbit coupling effects. This phenomenon revisits years of controversies and opens a new window into the challenge of manipulating spin degree of freedom in future information-processing technologies.
Pseudospin-driven spin relaxation mechanism in graphene
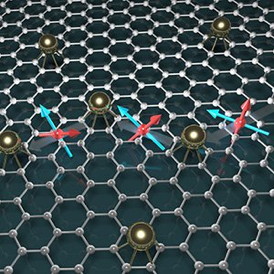
Barcelona, Spain | Posted on November 11th, 2014The prospect of transporting spin information over long distances in graphene, possible because of its small intrinsic spin-orbit coupling and vanishing hyperfine interaction, has stimulated intense research exploring spintronics applications. However, measured spin relaxation times are orders of magnitude smaller than initially predicted, while the main physical process for spin dephasing and its charge-density and disorder dependences remain unconvincingly described by conventional mechanisms.
In a recent publication in Nature Physics, ICN2 researchers unravel an unprecedented spin relaxation mechanism for non-magnetic samples that follows from an entanglement between spin and pseudospin driven by random spin-orbit coupling, unique to graphene. The work was led by ICREA Research Prof. Stephan Roche, Group Leader of the ICN2 Theoretical and Computational Nanoscience Group. The first author of the paper is Dr. Dinh Van Tuan, from the Group led by Prof. Roche, and ICREA Research Prof. Sergio O. Valenzuela, Group Leader of the ICN2 Physics and Engineering of Nanodevices Group, is among the authors.
The mixing between spin and pseudospin-related Berry's phases results in fast spin dephasing even when approaching the ballistic limit, with increasing relaxation times away from the Dirac point, as observed experimentally. The origin of spin-orbit coupling can stem from by adatoms, ripples or even the substrate, suggesting novel spin manipulation strategies based on the pseudospin degree of freedom.
Such possibilities suggest unprecedented approaches for the emergence of non-charge-based information processing and computing, resulting in a new generation of active (CMOS compatible) spintronic devices together with non-volatile low-energy MRAM memories. This phenomenon not only revisits years of experimental and theoretical controversies, but also opens a new window into the formidable challenge of manipulating spin degree of freedom in future information-processing technologies.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Àlex Argemí
Phone: +34937372607
Copyright © ICN2
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Spintronics
![]() Quantum materials: Electron spin measured for the first time June 9th, 2023
Quantum materials: Electron spin measured for the first time June 9th, 2023
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Quantum Computing
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Quantum nanoscience
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








