Home > Press > Supersonic spray delivers high quality graphene layer
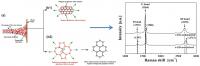 |
| Using a supersonic spray, graphene flakes with deformed pentagonal and heptagonal structures stretch on impact and spring into a perfect hexagonal graphene lattice. This opens the way to scale up from the microscopic to large scale applications.
Credit: Photo credit: Suman Sinha-Ray |
Abstract:
A simple, inexpensive spray method that deposits a graphene film can heal manufacturing defects and produce a high quality graphene layer on a range of substrates, report researchers at the University of Illinois at Chicago and Korea University.
Supersonic spray delivers high quality graphene layer
Chicago, IL | Posted on May 28th, 2014Their study is available online in the journal Advanced Functional Materials.
Graphene, a two-dimensional wonder-material composed of a single layer of carbon atoms, is strong, transparent, and an excellent conductor of electricity. It has potential in a wide range of applications, such as reinforcing and lending electrical properties to plastics; creating denser and faster integrated circuits; and building better touch screens.
Although the potential uses for graphene seem limitless, there has been no easy way to scale up from microscopic to large-scale applications without introducing defects, says Alexander Yarin, UIC professor of mechanical and industrial engineering and co-principal investigator on the study.
"Normally, graphene is produced in small flakes, and even these small flakes have defects," Yarin said. Worse, when you try to deposit them onto a large-scale area, defects increase, and graphene's useful properties its "magic" are lost, he said.
Yarin first turned to solving how to deposit graphene flakes to form a consistent layer without any clumps or spaces. He went to Sam S. Yoon, professor of mechanical engineering at Korea University and co-principal investigator on the study.
Yoon had been working with a unique kinetic spray deposition system that exploits the supersonic acceleration of droplets through a Laval nozzle. Although Yoon was working with different materials, Yarin believed his method might be used to deposit graphene flakes into a smooth layer.
Their supersonic spray system produces very small droplets of graphene suspension, which disperse evenly, evaporate rapidly, and reduce the tendency of the graphene flakes to aggregate.
But to the researchers' surprise, defects inherent in the flakes themselves disappeared, as a by-product of the spray method. The result was a higher quality graphene layer, as found in the analysis by another collaborator, Suman Sinha-Ray, senior researcher at United States Gypsum and UIC adjunct professor of mechanical and industrial engineering.
The researchers demonstrated that the energy of the impact stretches the graphene and restructures the arrangement of its carbon atoms into the perfect hexagons of flawless graphene.
"Imagine something like Silly Putty hitting a wall it stretches out and spreads smoothly," said Yarin. "That's what we believe happens with these graphene flakes. They hit with enormous kinetic energy, and stretch in all directions.
"We're tapping into graphene's plasticity it's actually restructuring."
Other attempts to produce graphene without defects or to remove flaws after manufacture have proved difficult and prohibitively expensive, Yarin said.
The new method of deposition, which allows graphene to "heal" its defects during application, is simple, inexpensive, and can be performed on any substrate with no need for post-treatment, he said.
Yarin and his Korean colleagues hope to continue their successful collaboration and foster the development of industrial-scale applications of graphene.
###
Jung-Jae Park, Jung-Gun Lee and You-Hong Cha of Korea University; Sang-Hoon Bae and Jong-Hyun Ahn of Yonsei University; and Yong Chae Jung and Soo Min Kim of the Korea Institute of Science and Technology are co-authors on the paper.
Initial support for the collaboration between Yarin's group at UIC and Yoon's group at Korean University was provided by the Office of International Affairs Nuveen International Development Fund at UIC and by Korea University.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Jeanne Galatzer-Levy
312-996-1583
Copyright © University of Illinois at Chicago
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Industrial
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() Quantum interference in molecule-surface collisions February 28th, 2025
Quantum interference in molecule-surface collisions February 28th, 2025
![]() Boron nitride nanotube fibers get real: Rice lab creates first heat-tolerant, stable fibers from wet-spinning process June 24th, 2022
Boron nitride nanotube fibers get real: Rice lab creates first heat-tolerant, stable fibers from wet-spinning process June 24th, 2022
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








