Home > Press > Berkeley Lab Researchers Demonstrate First Size-based Chromatography Technique for the Study of Living Cells
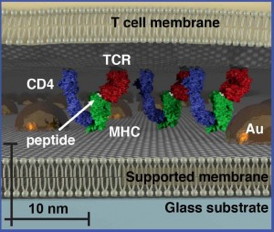 |
| With size-based chromatography, a hexagonally ordered array of gold nanoparticles is fabricated onto a hybrid live cell-supported membrane. Membrane components move freely through the array provided they don’t exceed its physical dimensions. This reveals organizational aspects of the membrane environment unobservable by other techniques. |
Abstract:
Using nanodot technology, Berkeley Lab researchers have demonstrated the first size-based form of chromatography that can be used to study the membranes of living cells. This unique physical approach to probing cellular membrane structures can reveal information critical to whether a cell lives or dies, remains normal or turns cancerous, that can't be obtained through conventional microscopy.
Berkeley Lab Researchers Demonstrate First Size-based Chromatography Technique for the Study of Living Cells
Berkeley, CA | Posted on April 22nd, 2014"We've developed membrane-embedded nanodot array platforms that provide a physical means to both probe and manipulate membrane assemblies, including signaling clusters, while they are functioning in the membrane of a living cell," says Jay Groves, a chemist with Berkeley Lab's Physical Biosciences Division, who led this research.
Groves, who is also a professor with the University of California (UC) Berkeley's Chemistry Department, and a Howard Hughes Medical Institute (HHMI) investigator, is a recognized leader in developing techniques for studying the impact of spatial patterns on living cells. The live-cell supported synthetic membranes he and his group have been developing are constructed out of lipids and assembled onto a substrate of solid silica. These membranes are being used to determine how living cells not only interact with their environment through chemical signals but also through physical force and spatial patterns.
"We call our approach the spatial mutation strategy because molecules in a cell can be spatially re-arranged without altering the cell in any other way," Groves says. "Our live cell-supported membranes provide a hybrid interface consisting of mobile and immobile components with controlled geometry that allows us to utilize solid-state nanotechnology to manipulate and control molecular systems inside living cells."
While the work of Groves and others in recent years has demonstrated the importance of protein and lipid spatial organization within cellular membranes, details as to how spatial organization is tied to function are scarce primarily because of the limitations of optical microscopy at length scales below the 250 nanometer diffraction limit. The size-based chromatography technique developed by Groves and his group allows them to probe supramolecular structures in a cell membrane at the needed nanometer length-scales.
"We now have a way to translate nano-sized structures that approach molecular dimensions into geometric constraints on the movement of molecules inside a living cell," Groves says.
For their size-based chromatography technique, the spacing of proteins and other cellular molecules is controlled by a hexagonal or honeycomb array of gold nanoparticles that is fabricated into the membrane. The spacing between nanoparticles in each array can be controlled, with accessible sizes ranging from 30 to nearly 200 nanometers.
"Individual membrane components move freely throughout the array, but movement of larger assemblies is impeded if they exceed the physical dimensions of the array, Groves says.
Groves and his colleagues tested their size-based chromatography technique on T cell receptor (TCR) microclusters in T cell membranes, which is the functional module for antigen recognition by T cells (lymphocytes from the thymus) in the body's immune system. These TCR signaling clusters occupy a size regime ranging from tens to a few hundred nanometers, which is typically below the diffraction limit of conventional optical microscopy. Size-based chromatography was used to probe the physical properties of TCR signaling clusters as a function of antigen density. The results revealed that TCR signaling cluster is distinctly dependent on the amount of antigen encountered by the cell.
"This is something we did not know before about the TCR microcluster signaling system, which has been well-studied using conventional optical microscopy," Groves says. "It is a proof-of-principle demonstration that represents another step in the direction of interfacing living cells with synthetic materials to achieve molecular level control of the cell."
A paper on this research has been published in NANO Letters. The paper is titled "Size-based chromatography of signaling clusters in a living cell membrane." Groves is the corresponding author. Others authors are Niña Caculitan, Hiroyuki Kai, Eulanca Liu, Nicole Fay, Yan Yu, Theobald Lohmüller and Geoff O'Donoghue.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Lynn Yarris
(510) 486-5375
Copyright © DOE/Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() For more about the research of Jay Groves go here:
For more about the research of Jay Groves go here:
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








