Home > Press > Thinnest feasible membrane produced
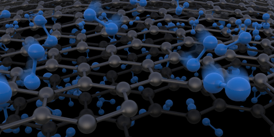 |
| Artist’s rendering of the two-layered graphene membrane (grey honeycomb structure) with molecules (blue) being able – as a function of their size – to pass the pores. Illustration: Ben Newton / ETH Zurich |
Abstract:
Researchers have produced a stable porous membrane that is thinner than a nanometre. This is a 100,000 times thinner than the diameter of a human hair. The membrane consists of two layers of the much exalted "super material" graphene, a two-dimensional film made of carbon atoms, on which the team of researchers, led by Professor Hyung Gyu Park at the Department of Mechanical and Process Engineering at ETH Zurich, etched tiny pores of a precisely defined size.
Thinnest feasible membrane produced
Zurich, Switzerland | Posted on April 17th, 2014The membrane can thus permeate tiny molecules. Larger molecules or particles, on the other hand, can pass only slowly or not at all. "With a thickness of just two carbon atoms, this is the thinnest porous membrane that is technologically possible to make," says PhD student Jakob Buchheim, one of the two lead authors of the study, which was conducted by ETH-Zurich researchers in collaboration with scientists from Empa and a research laboratory of LG Electronics. The study has just been published in journal Science.
The ultra-thin graphene membrane may one day be used for a range of different purposes, including waterproof clothing. "Our membrane is not only very light and flexible, but it is also a thousand fold more breathable than Goretex," says Kemal Celebi, a postdoc in Park's laboratory and also one of the lead authors of the study. The membrane could also potentially be used to separate gaseous mixtures into their constituent parts or to filter impurities from fluids. The researchers were able to demonstrate for the first time that graphene membranes could be suitable for water filtration. The researchers also see a potential use for the membrane in devices used for the accurate measurement of gas and fluid flow rates that are crucial to unveiling the physics around mass transfer at nanoscales and separation of chemical mixtures.
Breakthrough in nanofabrication
The researchers not only succeeded in producing the starting material, a double-layer graphene film with a high level of purity, but they also mastered a technique called focused ion beam milling to etch pores into the graphene film. In this process, which is also used in the production of semiconductors, a beam of helium or gallium ions is controlled with a high level of precision in order to etch away material. The researchers were able to etch pores of a specified number and size into the graphene with unprecedented precision. This process, which could easily take days to complete, took only a few hours in the current work. "This is a breakthrough that enables the nanofabrication of the porous graphene membranes," explains Ivan Shorubalko, a scientist at Empa that also contributed to the study.
In order to achieve this level of precision, the researchers had to work with double-layer graphene. "It wouldn't have been possible for this method to create such a membrane with only one layer because graphene in practice isn't perfect," says Park. The material can exhibit certain irregularities in the honeycomb structure of the carbon atoms. Now and again, individual atoms are missing from the structure, which not only impairs the stability of the material but also makes it impossible to etch a high-precision pore onto such a defect. The researchers solved this problem by laying two graphene layers on top of each other. The probability of two defects settling directly above one another is extremely low, explains Park.
Fastest possible filtration
A key advantage of the tiny dimensions is that the thinner a membrane, the lower its permeation resistance. The lower the resistance, the higher the energy-efficiency of the filtration process. "With such atomically thin membranes we can reach maximal permeation for a membrane of a given pore size and we believe that they allow the fastest feasible rate of permeation," says Celebi. However, before these applications are ready for use on an industrial scale or for the production of functional waterproof clothing, the manufacturing process needs to be further developed. To investigate the fundamental science, the researchers worked with tiny pieces of membrane with a surface area of less than one hundredth of a square millimetre. Objectives from now on will be to produce larger membrane surfaces and impose various filtering mechanisms.
####
About ETH Zurich
ETH Zurich is one of the leading international universities for technology and the natural sciences. It is well-known for its excellent education, ground-breaking fundamental research and for implementing its results directly into practice.
Founded in 1855, ETH Zurich today has more than 18,000 students from over 110 countries, including 3,900 doctoral students. To researchers, it offers an inspiring working environment, to students, a comprehensive education.
Twenty-one Nobel Laureates have studied, taught or conducted research at ETH Zurich, underlining the excellent reputation of the university.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Hyung Gyu Park
41-446-329-460
Copyright © ETH Zurich
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
Chemistry
![]() Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Water
![]() Taking salt out of the water equation October 7th, 2022
Taking salt out of the water equation October 7th, 2022
Textiles/Clothing
![]() Protective equipment with graphene nanotubes meets the strictest ESD safety standards March 25th, 2022
Protective equipment with graphene nanotubes meets the strictest ESD safety standards March 25th, 2022
![]() Polymer fibers with graphene nanotubes make it possible to heat hard-to-reach, complex-shaped items February 11th, 2022
Polymer fibers with graphene nanotubes make it possible to heat hard-to-reach, complex-shaped items February 11th, 2022
![]() Flexible material shows potential for use in fabrics to heat, cool July 3rd, 2020
Flexible material shows potential for use in fabrics to heat, cool July 3rd, 2020
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








