Home > Press > Biologists Develop Nanosensors to Visualize Movements and Distribution of Plant Stress Hormone
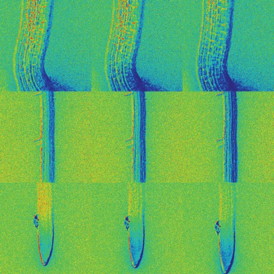 |
| Time sequence shows how mustard seedlings take up and distribute ABA through roots and other parts of the plant during germination. Credit: Rainer Waadt, UC San Diego |
Abstract:
Biologists at UC San Diego have succeeded in visualizing the movement within plants of a key hormone responsible for growth and resistance to drought. The achievement will allow researchers to conduct further studies to determine how the hormone helps plants respond to drought and other environmental stresses driven by the continuing increase in the atmosphere's carbon dioxide, or CO2, concentration.
Biologists Develop Nanosensors to Visualize Movements and Distribution of Plant Stress Hormone
San Diego, CA | Posted on April 15th, 2014The plant hormone the biologists directly tracked is abscisic acid, or ABA, which plays a major role in activating drought resistance responses of plants and in regulating plant growth under environmental stress conditions. The ABA stress hormone also controls the closing of stomata, the pores within leaves through which plants lose 95 percent of their water while taking in CO2 for growth.
Scientists already know the general role that ABA plays within plants, but by directly visualizing the hormone they can now better understand the complex interactions involving ABA when a plant is subjected to drought or other stress.
"Understanding the dynamic distribution of ABA in plants in response to environmental stimuli is of particular importance in elucidating the action of this important plant hormone," says Julian Schroeder, a professor of biology at UC San Diego who headed the research effort. "For example, we can now investigate whether an increase in the leaf CO2 concentration that occurs every night due to respiration in leaves affects the ABA concentration in stomatal cells."
The researchers developed what they call a "genetically-encoded reporter" in order to directly and instantaneously observe the movements of ABA within the mustard plant Arabidopsis. These reporters, called "ABAleons," contain two differentially colored fluorescent proteins attached to an ABA-binding sensor protein. Once bound to ABA, the ABAleons change their fluorescence emission, which can be analyzed using a microscope. The researchers showed that ABA concentration changes and waves of ABA movement could be monitored in diverse tissues and individual cells over time and in response to stress.
"Using this reporter, we directly observed long distance ABA movements from the stem of a germinating seedling to the leaves and roots of the growing plant and, for the first time, we were able to determine the rate of ABA movement within the growing plant," says Schroeder.
"Using this tool, we now can detect ABA in live plants and see how it is distributed," says Rainer Waadt, a postdoctoral associate in Schroeder's laboratory and the first author of the paper. "We are also able to directly see that environmental stress causes an increase in the ABA concentration in the stomatal guard cells that surround each stomatal pore. In the future, our sensors can be used to study ABA distribution in response to different stresses, including CO2 elevations, and to identify other molecules and proteins that affect the distribution of this hormone. We can also learn how fast plants respond to stresses and which tissues are important for the response."
The researchers demonstrated that their new ABA nanosensors also function effectively as isolated proteins. This means that the sensors could be directly employed using state-of-the-art high-throughput screening platforms to screen for chemicals that could activate or enhance a drought resistance response. The scientists say such chemicals could become useful in the future for enhancing a drought resistance response, when crops experience a severe drought, like the one that occurred in the Midwest in the summer of 2012.
The study was supported by grants from the National Science Foundation and, in part, the National Institutes of Health and the U.S Department of Energy's Division of Chemical Sciences, Geosciences, and Biosciences in the Office of Basic Energy Sciences.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Kim McDonald
858-534-7572
Copyright © University of California - San Diego
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Videos/Movies
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() New X-ray imaging technique to study the transient phases of quantum materials December 29th, 2022
New X-ray imaging technique to study the transient phases of quantum materials December 29th, 2022
![]() Solvent study solves solar cell durability puzzle: Rice-led project could make perovskite cells ready for prime time September 23rd, 2022
Solvent study solves solar cell durability puzzle: Rice-led project could make perovskite cells ready for prime time September 23rd, 2022
![]() Scientists prepare for the world’s smallest race: Nanocar Race II March 18th, 2022
Scientists prepare for the world’s smallest race: Nanocar Race II March 18th, 2022
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Food/Agriculture/Supplements
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() SMART researchers pioneer first-of-its-kind nanosensor for real-time iron detection in plants February 28th, 2025
SMART researchers pioneer first-of-its-kind nanosensor for real-time iron detection in plants February 28th, 2025
![]() Silver nanoparticles: guaranteeing antimicrobial safe-tea November 17th, 2023
Silver nanoparticles: guaranteeing antimicrobial safe-tea November 17th, 2023
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








