Home > Press > Shiny quantum dots brighten future of solar cells: Photovoltaic solar-panel windows could be next for your house
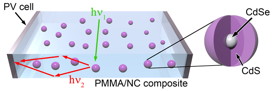 |
| This schematic shows how the quantum dots are embedded in the plastic matrix and capture sunlight to improve solar panel efficiency. |
Abstract:
A house window that doubles as a solar panel could be on the horizon, thanks to recent quantum-dot work by Los Alamos National Laboratory researchers in collaboration with scientists from University of Milano-Bicocca (UNIMIB), Italy. Their project demonstrates that superior light-emitting properties of quantum dots can be applied in solar energy by helping more efficiently harvest sunlight.
Shiny quantum dots brighten future of solar cells: Photovoltaic solar-panel windows could be next for your house
Los Alamos, NM | Posted on April 14th, 2014"The key accomplishment is the demonstration of large-area luminescent solar concentrators that use a new generation of specially engineered quantum dots," said lead researcher Victor Klimov of the Center for Advanced Solar Photophysics (CASP) at Los Alamos.
Quantum dots are ultra-small bits of semiconductor matter that can be synthesized with nearly atomic precision via modern methods of colloidal chemistry. Their emission color can be tuned by simply varying their dimensions. Color tunability is combined with high emission efficiencies approaching 100 percent. These properties have recently become the basis of a new technology - quantum dot displays - employed, for example, in the newest generation of the Kindle Fire ™ e-reader.
Light-harvesting antennas
A luminescent solar concentrator (LSC) is a photon management device, representing a slab of transparent material that contains highly efficient emitters such as dye molecules or quantum dots. Sunlight absorbed in the slab is re-radiated at longer wavelengths and guided towards the slab edge equipped with a solar cell.
Klimov explained, "The LSC serves as a light-harvesting antenna which concentrates solar radiation collected from a large area onto a much smaller solar cell, and this increases its power output."
"LSCs are especially attractive because in addition to gains in efficiency, they can enable new interesting concepts such as photovoltaic windows that can transform house facades into large-area energy generation units," said Sergio Brovelli, who worked at Los Alamos until 2012 and is now a faculty member at UNIMIB.
Because of highly efficient, color-tunable emission and solution processability, quantum dots are attractive materials for use in inexpensive, large-area LSCs. One challenge, however, is an overlap between emission and absorption bands in the dots, which leads to significant light losses due to the dots re-absorbing some of the light they produce.
"Giant" but still tiny, engineered dots
To overcome this problem the Los Alamos and UNIMIB researchers have developed LSCs based on quantum dots with artificially induced large separation between emission and absorption bands (called a large Stokes shift).
These "Stokes-shift" engineered quantum dots represent cadmium selenide/cadmium sulfide (CdSe/CdS) structures in which light absorption is dominated by an ultra-thick outer shell of CdS, while emission occurs from the inner core of a narrower-gap CdSe. The separation of light-absorption and light-emission functions between the two different parts of the nanostructure results in a large spectral shift of emission with respect to absorption, which greatly reduces losses to re-absorption.
To implement this concept, Los Alamos researchers created a series of thick-shell (so-called "giant") CdSe/CdS quantum dots, which were incorporated by their Italian partners into large slabs (sized in tens of centimeters) of polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA). While being large by quantum dot standards, the active particles are still tiny - only about hundred angstroms across. For comparison, a human hair is about 500,000 angstroms wide.
"A key to the success of this project was the use of a modified industrial method of cell-casting, we developed at UNIMIB Materials Science Department" said Francesco Meinardi, professor of Physics at UNIMIB.
Spectroscopic measurements indicated virtually no losses to re-absorption on distances of tens of centimeters. Further, tests using simulated solar radiation demonstrated high photon harvesting efficiencies of approximately 10% per absorbed photon achievable in nearly transparent samples, perfectly suited for utilization as photovoltaic windows.
Despite their high transparency, the fabricated structures showed significant enhancement of solar flux with the concentration factor of more than four. These exciting results indicate that "Stokes-shift-engineered" quantum dots represent a promising materials platform. It may enable the creation of solution processable large-area LSCs with independently tunable emission and absorption spectra.
Publication: A research paper, "Large-area luminescent solar concentrators based on ‘Stokes-shift-engineered' nanocrystals in a mass-polymerized PMMA matrix," is published online this week in Nature Photonics.
Funding: The Center for Advanced Solar Photophyscis (CASP) is an Energy Frontier Research Center funded by the Office of Science of the US Department of Energy.
The work of the UNIMIB team was conducted within the UNIMIB Department of Materials Science and funded by Fondazione Cariplo (2012-0844) and the European Community's Seventh Framework Programme (FP7/2007-2013; grant agreement no. 324603).
####
About Los Alamos National Laboratory
Los Alamos National Laboratory, a multidisciplinary research institution engaged in strategic science on behalf of national security, is operated by Los Alamos National Security, LLC, a team composed of Bechtel National, the University of California, The Babcock & Wilcox Company, and URS Corporation for the Department of Energy’s National Nuclear Security Administration.
Los Alamos enhances national security by ensuring the safety and reliability of the U.S. nuclear stockpile, developing technologies to reduce threats from weapons of mass destruction, and solving problems related to energy, environment, infrastructure, health, and global security concerns.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Nancy Ambrosiano
(505) 667-0471
Copyright © Los Alamos National Laboratory
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Industrial
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() Quantum interference in molecule-surface collisions February 28th, 2025
Quantum interference in molecule-surface collisions February 28th, 2025
![]() Boron nitride nanotube fibers get real: Rice lab creates first heat-tolerant, stable fibers from wet-spinning process June 24th, 2022
Boron nitride nanotube fibers get real: Rice lab creates first heat-tolerant, stable fibers from wet-spinning process June 24th, 2022
Quantum Dots/Rods
![]() A new kind of magnetism November 17th, 2023
A new kind of magnetism November 17th, 2023
![]() IOP Publishing celebrates World Quantum Day with the announcement of a special quantum collection and the winners of two prestigious quantum awards April 14th, 2023
IOP Publishing celebrates World Quantum Day with the announcement of a special quantum collection and the winners of two prestigious quantum awards April 14th, 2023
![]() Qubits on strong stimulants: Researchers find ways to improve the storage time of quantum information in a spin rich material January 27th, 2023
Qubits on strong stimulants: Researchers find ways to improve the storage time of quantum information in a spin rich material January 27th, 2023
![]() NIST’s grid of quantum islands could reveal secrets for powerful technologies November 18th, 2022
NIST’s grid of quantum islands could reveal secrets for powerful technologies November 18th, 2022
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
![]() Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








