Home > Press > Researchers Grow Carbon Nanofibers Using Ambient Air, Without Toxic Ammonia
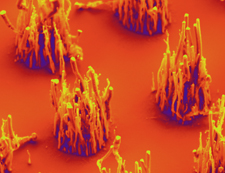 |
| Researchers have shown they can grow vertically-aligned carbon nanofibers using ambient air, rather than ammonia gas. Click to enlarge image. Credit: Anatoli Melechko. |
Abstract:
"Aerosynthesis: Growth of Vertically-aligned Carbon Nanofibres with Air DC Plasma"
Authors: A. Kodumagulla, V. Varanasi, R.C. Pearce, W.C. Wu, J.B. Tracy, and A.V. Melechko, North Carolina State University; D.K. Hensley and T.E. McKnight, Oak Ridge National Laboratory
Published: March 12, 2014, Nanomaterials and Nanotechnology
DOI: 10.5772/58449
Abstract: Vertically-aligned carbon nanofibres (VACNFs) have been synthesized in a mixture of acetone and air using catalytic DC plasma-enhanced chemical vapour deposition. Typically, ammonia or hydrogen is used as an etchant gas in the mixture to remove carbon that otherwise passivates the catalyst surface and impedes growth. Our demonstration of the use of air as the etchant gas opens up the possibility that ion etching could be sufficient to maintain the catalytic activity state during synthesis. It also demonstrates a path toward growing VACNFs in the open atmosphere.
Researchers Grow Carbon Nanofibers Using Ambient Air, Without Toxic Ammonia
Raleigh, NC | Posted on March 24th, 2014Researchers from North Carolina State University have demonstrated that vertically aligned carbon nanofibers (VACNFs) can be manufactured using ambient air, making the manufacturing process safer and less expensive. VACNFs hold promise for use in gene-delivery tools, sensors, batteries and other technologies.
Conventional techniques for creating VACNFs rely on the use of ammonia gas, which is toxic. And while ammonia gas is not expensive, it's not free.
"This discovery makes VACNF manufacture safer and cheaper, because you don't need to account for the risks and costs associated with ammonia gas," says Dr. Anatoli Melechko, an adjunct associate professor of materials science and engineering at NC State and senior author of a paper on the work. "This also raises the possibility of growing VACNFs on a much larger scale."
In the most common method for VACNF manufacture, a substrate coated with nickel nanoparticles is placed in a vacuum chamber and heated to 700 degrees Celsius. The chamber is then filled with ammonia gas and either acetylene or acetone gas, which contain carbon. When a voltage is applied to the substrate and a corresponding anode in the chamber, the gas is ionized. This creates plasma that directs the nanofiber growth. The nickel nanoparticles free carbon atoms, which begin forming VACNFs beneath the nickel catalyst nanoparticles. However, if too much carbon forms on the nanoparticles it can pile up and clog the passage of carbon atoms to the growing nanofibers.
Ammonia's role in this process is to keep carbon from forming a crust on the nanoparticles, which would prevent the formation of VACNFs.
"We didn't think we could grow VACNFs without ammonia or a hydrogen gas," Melechko says. But he tried anyway.
Melechko's team tried the conventional vacuum technique, using acetone gas. However, they replaced the ammonia gas with ambient air - and it worked. The size, shape and alignment of the VACNFs were consistent with the VACNFs produced using conventional techniques.
"We did this using the vacuum technique without ammonia," Melechko says. "But it creates the theoretical possibility of growing VACNFs without a vacuum chamber. If that can be done, you would be able to create VACNFs on a much larger scale."
Melechko also highlights the role of two high school students involved in the work: A. Kodumagulla and V. Varanasi, who are lead authors of the paper. "This discovery would not have happened if not for their approach to the problem, which was free from any preconceptions," Melechko says. "I think they're future materials engineers."
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Matt Shipman
919-515-6386
Copyright © North Carolina State University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
Chemistry
![]() Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Nanotubes/Buckyballs/Fullerenes/Nanorods/Nanostrings/Nanosheets
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








