Home > Press > Cellulose nanocrystals possible 'green' wonder material
 |
Abstract:
Anisotropy of the Elastic Properties of Crystalline Cellulose Iβ from First Principles Density Functional Theory with Van der Waals Interactions
Fernando L. Dri, Louis G. Hector Jr., Robert J. Moon, Pablo D. Zavattieri
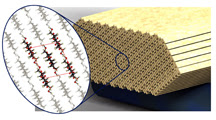
In spite of the significant potential of cellulose nanocrystals as functional nanoparticles for numerous applications, a fundamental understanding of the mechanical properties of defect-free, crystalline cellulose is still lacking. In this paper, the elasticity matrix for cellulose Iβ with hydrogen bonding network A was calculated using ab initio density functional theory with a semi-empirical correction for van der Waals interactions. The computed Young's modulus is found to be 206 GPa along [001] (c-axis), 98 GPa along [010] (b-axis), and 19 GPa along [100] (a-axis). Full compliance matrices are reported for 1.0, 1.5 and 2.0 % applied strains Color contour surfaces that show variations of the Young's modulus and average Poisson's ratio with crystallographic direction revealed the extreme anisotropies of these important mechanical properties. The sensitivity of the elastic parameters to misalignments in the crystal were examined with 2D polar plots within selected planes containing specific bonding characteristics; these are used to explain the substantial variability in the reported experimental Young's moduli values. Results for the lattice directions [001], [010] and [100] are within the range of reported experimental and other numerical values.
Cellulose nanocrystals possible 'green' wonder material
West Lafayette, IN | Posted on December 16th, 2013The same tiny cellulose crystals that give trees and plants their high strength, light weight and resilience, have now been shown to have the stiffness of steel.
The nanocrystals might be used to create a new class of biomaterials with wide-ranging applications, such as strengthening construction materials and automotive components.
Calculations using precise models based on the atomic structure of cellulose show the crystals have a stiffness of 206 gigapascals, which is comparable to steel, said Pablo D. Zavattieri, a Purdue University assistant professor of civil engineering.
"This is a material that is showing really amazing properties," he said. "It is abundant, renewable and produced as waste in the paper industry."
Findings are detailed in a research paper featured on the cover of the December issue of the journal Cellulose.
"It is very difficult to measure the properties of these crystals experimentally because they are really tiny," Zavattieri said. "For the first time, we predicted their properties using quantum mechanics."
The nanocrystals are about 3 nanometers wide by 500 nanometers long - or about 1/1,000th the width of a grain of sand - making them too small to study with light microscopes and difficult to measure with laboratory instruments.
The paper was authored by Purdue doctoral student Fernando L. Dri; Louis G. Hector Jr., a researcher from the Chemical Sciences and Materials Systems Laboratory at General Motors Research and Development Center; Robert J. Moon, a researcher from the U.S. Forest Service's Forest Products Laboratory; and Zavattieri.
The findings represent a milestone in understanding the fundamental mechanical behavior of the cellulose nanocrystals.
"It is also the first step towards a multiscale modeling approach to understand and predict the behavior of individual crystals, the interaction between them, and their interaction with other materials," Zavattieri said. "This is important for the design of novel cellulose-based materials as other research groups are considering them for a huge variety of applications, ranging from electronics and medical devices to structural components for the automotive, civil and aerospace industries."
The cellulose nanocrystals represent a potential green alternative to carbon nanotubes for reinforcing materials such as polymers and concrete. Applications for biomaterials made from the cellulose nanocrystals might include biodegradable plastic bags, textiles and wound dressings; flexible batteries made from electrically conductive paper; new drug-delivery technologies; transparent flexible displays for electronic devices; special filters for water purification; new types of sensors; and computer memory.
Cellulose could come from a variety of biological sources including trees, plants, algae, ocean-dwelling organisms called tunicates, and bacteria that create a protective web of cellulose.
"With this in mind, cellulose nanomaterials are inherently renewable, sustainable, biodegradable and carbon-neutral like the sources from which they were extracted," Moon said. "They have the potential to be processed at industrial-scale quantities and at low cost compared to other materials."
Biomaterials manufacturing could be a natural extension of the paper and biofuels industries, using technology that is already well-established for cellulose-based materials.
"Some of the byproducts of the paper industry now go to making biofuels, so we could just add another process to use the leftover cellulose to make a composite material," Moon said. "The cellulose crystals are more difficult to break down into sugars to make liquid fuel. So let's make a product out of it, building on the existing infrastructure of the pulp and paper industry."
Their surface can be chemically modified to achieve different surface properties.
"For example, you might want to modify the surface so that it binds strongly with a reinforcing polymer to make a new type of tough composite material, or you might want to change the chemical characteristics so that it behaves differently with its environment," Moon said.
Zavattieri plans to extend his research to study the properties of alpha-chitin, a material from the shells of organisms including lobsters, crabs, mollusks and insects. Alpha-chitin appears to have similar mechanical properties as cellulose.
"This material is also abundant, renewable and waste of the food industry," he said.
The research was funded by the Forest Products Laboratory through the U.S. Department of Agriculture, the Purdue Research Foundation and the National Science Foundation.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Writer:
Emil Venere
765-494-4709
Sources:
Pablo D. Zavattieri
765-496-9644
Robert Moon
Copyright © Purdue University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Food/Agriculture/Supplements
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() SMART researchers pioneer first-of-its-kind nanosensor for real-time iron detection in plants February 28th, 2025
SMART researchers pioneer first-of-its-kind nanosensor for real-time iron detection in plants February 28th, 2025
![]() Silver nanoparticles: guaranteeing antimicrobial safe-tea November 17th, 2023
Silver nanoparticles: guaranteeing antimicrobial safe-tea November 17th, 2023
Automotive/Transportation
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Construction
![]() Temperature-sensing building material changes color to save energy January 27th, 2023
Temperature-sensing building material changes color to save energy January 27th, 2023
![]() Strain-sensing smart skin ready to deploy: Nanotube-embedded coating detects threats from wear and tear in large structures July 15th, 2022
Strain-sensing smart skin ready to deploy: Nanotube-embedded coating detects threats from wear and tear in large structures July 15th, 2022
![]() A sunlight-driven “self-healing” anti-corrosion coating May 27th, 2022
A sunlight-driven “self-healing” anti-corrosion coating May 27th, 2022
![]() Polymer fibers with graphene nanotubes make it possible to heat hard-to-reach, complex-shaped items February 11th, 2022
Polymer fibers with graphene nanotubes make it possible to heat hard-to-reach, complex-shaped items February 11th, 2022
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








