Home > Press > KAIST developed the biotemplated design of piezoelectric energy harvesting device
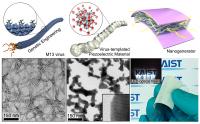 |
| First row: Schemes of each step to explain biotemplated nanogenerator fabrication by using genetically engineered virus. Second row: Electron microscopy of each step in biotemplated synthetic processes and digital photograph of the flexible biotemplated nanogenerator. Right inset shows the driven LED optical fibers by the energy harvester.
Credit: KAIST |
Abstract:
A research team led by Professor Keon Jae Lee and Professor Yoon Sung Nam from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at KAIST has developed the biotemplated design of flexible piezoelectric energy harvesting device, called "nanogenerator."
KAIST developed the biotemplated design of piezoelectric energy harvesting device
Ulsan, Korea | Posted on December 3rd, 2013Nature has its own capabilities to spontaneously synthesize and self-assemble universal materials with sophisticated architectures such as shells, sea sponges, and bone minerals. For instance, the natural sea shell, consisting of calcium carbonate (CaCO3), is very rigid and tough whereas the artificial chalk made by the same material is fragile. In addition, most of artificial syntheses are performed under toxic, expensive and extreme environments in contrast to the natural syntheses, which are processed in benign and mild surroundings. If human can mimic these biological abilities, a variety of ecological and material issues can be solved.
The KAIST team modified a M13 viral gene, which is harmless to human and widely exist in nature, to utilize its remarkable ability of synthesizing a highly piezoelectric inorganic material, barium titanate (BaTiO3). By using this biotemplated piezoelectric material, a high-output flexible nanogenerator could be fabricated with an enhanced performance. The flexible piezoelectric nanogenerator that converts mechanical energy of tiny movements into electrical energy is an attractive candidate for the next generation energy harvesting technology. This biotemplated nanogenerator will drive commercial LCD screens and LED bulbs by simple finger movements.
Professor Lee said, "This is the first time to introduce a biotemplated inorganic piezoelectric material to a self-powered energy harvesting system, which can be realized through eco-friendly and efficient material syntheses."
###
The research result was published in the November online issue of the American Chemical Society's journal, ACS Nano (Virus-Directed Design of a Flexible BaTiO3 Nanogenerator). In addition, the team also extended their research to a large-area and mass producible "PZT based nanocomposite generator," which was published in the December issue of Advanced Energy Materials, a Wiley-VCH journal.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Lan Yoon
82-423-502-294
Copyright © The Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Display technology/LEDs/SS Lighting/OLEDs
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Discoveries
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Announcements
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Deciphering local microstrain-induced optimization of asymmetric Fe single atomic sites for efficient oxygen reduction August 8th, 2025
Deciphering local microstrain-induced optimization of asymmetric Fe single atomic sites for efficient oxygen reduction August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








