Home > Press > Whirlpools on the Nanoscale Could Multiply Magnetic Memory: At the Advanced Light Source, Berkeley Lab scientists join an international team to control spin orientation in magnetic nanodisks
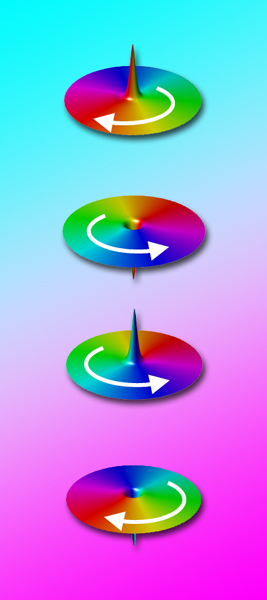 |
| The electron spins in a magnetic vortex all point in parallel, either clockwise or counterclockwise. Spins in the crowded core of the vortex must point out of the plane, either up or down. The four orientations of circularity and polarity could form the cells of multibit magnetic storage and processing systems. |
Abstract:
"We spent 15 percent of home energy on gadgets in 2009, and we're buying more gadgets all the time," says Peter Fischer of the U.S. Department of Energy's Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab). Fischer lets you know right away that while it's scientific curiosity that inspires his research at the Lab's Advanced Light Source (ALS), he intends it to help solve pressing problems.
Whirlpools on the Nanoscale Could Multiply Magnetic Memory: At the Advanced Light Source, Berkeley Lab scientists join an international team to control spin orientation in magnetic nanodisks
Berkeley, CA | Posted on May 22nd, 2013"What we're working on now could make these gadgets perform hundreds of times better and also be a hundred times more energy efficient," says Fischer, a staff scientist in the Materials Sciences Division. As a principal investigator at the Center for X-Ray Optics, he leads ALS beamline 6.1.2, where he specializes in studies of magnetism.
Fischer recently provided critical support to a team led by Vojtĕch Uhlíř of the Brno University of Technology in the Czech Republic and the Center for Magnetic Recording Research at the University of California, San Diego. Researchers from both institutions and from Berkeley Lab used the unique capabilities of beamline 6.1.2 to advance a new concept in magnetic memory.
"Magnetic memory is at the heart of most electronic devices," says Fischer, "and from the scientist's point of view, magnetism is about controlling electron spin."
Magnetic memories store bits of information in discrete units whose electron spins all line up in parallel, pointing one way or the opposite to signify a one or a zero. What Fischer and his colleagues propose is multibit storage in which each unit has four states instead of two and can store twice the information.
The key is magnetic vortices - whirlpools of magnetic field - confined to tiny metal disks a few billionths of a meter (nanometers) in diameter. The electron spins are seeking the lowest possible energy; spins that point in opposing directions, antiparallel, cost energy. Thus the electrons line up with all their spins pointing in a circle, either clockwise or counterclockwise around the disk.
In the core of the vortex, however, where the circles get smaller and smaller and neighboring spins would inevitably align antiparallel, they tend to tilt out of the plane, pointing either up or down.
"So each disk has four bits instead of two - left or right circularity and up or down polarity of the core - but you must be able to control the orientation of each independently," says Fischer.
Up, down, and around - taking control
Applying a strong, steady external magnetic field can reverse core polarity, but practical devices can't tolerate strong fields, and they need faster switches. Previous researchers at the ALS had found that with weak oscillating magnetic fields in the plane of the nanodisk they could quickly nudge the core out of its central position and get the same result.
"Instead of a static field, you wiggle it," Fischer explains. As the core is pushed away from the center of the disk, successive magnetic waves - changes in spin orientation - move the core faster and faster until its polarity flips to the opposite orientation.
The team used ALS beamline 6.1.2 to demonstrate, for the first time, that similar methods can control the circularity of the magnetic vortices.
In this case, the "wiggle" drives the core right off the edge of the disk. Once it's expelled, the vortex collapses and reforms, with spins pointing in the opposite direction: clockwise instead of counterclockwise, or vice versa.
Beamline 6.1.2 specializes in soft x-ray transmission microscopy of magnetic states, which allowed the researchers to make direct images of how the strength and duration of the trains of electric and magnetic pulses affected the circularity of the vortex. They found that control depends on the disk's geometry.
The disks were all tapered, with diagonal slices off their top surfaces that served to accelerate the core, once it started moving. But thickness and diameter were the important factors: the smaller the disk, the better.
"Thick" disks (30 nanometers) over a thousand nanometers in diameter were sluggards, taking more than three nanoseconds to switch circularity. But disks only 20 nanometers thick and 100 nanometers across could switch orientation in less than half a nanosecond.
Much remains to be done before the four-value multibit becomes practical, Polarity can be controlled, and circularity can be controlled, but so far they can't be controlled at the same time. Plans for doing this are in the works.
"This is the scientific basis for possible applications to come," says Fischer. "We are already looking at ways to control spin with temperature and voltage, at how to completely decouple spin from charge currents, and even at ways to couple chains of nanodisks together to build logic devices - not just for memory, but for computation."
In Fischer's opinion, the ALS's soft x-ray microscopes tools are in the pole position for the race in magnetism research. "No method besides x-ray microscopy can provide similarly comprehensive information, both to identify the magnetic materials and to image the fastest dynamics of magnetic states on the nanoscale. The instruments we have are unique and serve the whole vortex community, world-wide."
DOE's Office of Science supports the ALS and, with the European Regional Development Fund and the Grant Agency of the Czech Republic, supported this research.
####
About DOE/Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory
Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory addresses the world’s most urgent scientific challenges by advancing sustainable energy, protecting human health, creating new materials, and revealing the origin and fate of the universe. Founded in 1931, Berkeley Lab’s scientific expertise has been recognized with 13 Nobel prizes. The University of California manages Berkeley Lab for the U.S. Department of Energy’s Office of Science. For more, visit www.lbl.gov.
The Advanced Light Source is a third-generation synchrotron light source producing light in the x-ray region of the spectrum that is a billion times brighter than the sun. A DOE national user facility, the ALS attracts scientists from around the world and supports its users in doing outstanding science in a safe environment. For more information visit www-als.lbl.gov/.
DOE’s Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States, and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, please visit the Office of Science website at science.energy.gov.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Paul Preuss
510-486-6249
Copyright © DOE/Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() For more about Fischer’s research on magnetic vortices, visit:
For more about Fischer’s research on magnetic vortices, visit:
![]() Visit for more about the Center for X-Ray Optics:
Visit for more about the Center for X-Ray Optics:
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Spintronics
![]() Quantum materials: Electron spin measured for the first time June 9th, 2023
Quantum materials: Electron spin measured for the first time June 9th, 2023
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Memory Technology
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








