Home > Press > New magnetic graphene may revolutionise electronics
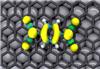 |
| Topographic STM images of a TCNQ monolayer on graphene/Ru. / IMDEA-Nanoscience |
Abstract:
Researchers from IMDEA-Nanociencia Institute and from Autonoma and Complutense Universities of Madrid (Spain) have managed to give graphene magnetic properties. The breakthrough, published in the journal 'Nature Physics', opens the door to the development of graphene-based spintronic devices, that is, devices based on the spin or rotation of the electron, and could transform the electronics industry.
New magnetic graphene may revolutionise electronics
Madrid, Spain | Posted on May 11th, 2013Scientists were already aware that graphene, an incredible material formed of a mesh of hexagonal carbon atoms, has extraordinary conductivity, mechanical and optical properties. Now it is possible to give it yet one more property: magnetism, implying a breakthrough in electronics.
This is revealed in the study that the Madrid Institute for Advanced Studies in Nanoscience (IMDEA-Nanociencia) and Autonoma Autonomous (UAM) and Complutense (UCM) universities of Madrid have just published in the 'Nature Physics' journal. Researchers have managed to create a hybrid surface from this material that behaves as a magnet.
"In spite of the huge efforts to date of scientists all over the world, it has not been possible to add the magnetic properties required to develop graphene-based spintronics. However these results pave the way to this possibility," highlights Prof. Rodolfo Miranda, Director of IMDEA-Nanociencia.
Spintronics is based on the charge of the electron, as in traditional electronics, but also on its spin, which determines its magnetic moment. A material is magnetic when most of its electrons have the same spin.
As the spin can have two values, its use adds two more states to traditional electronics. Thus, both data processing speed and quantity of data to be stored on electronic devices can be increased, with applications in fields such as telecommunications, computing, energy and biomedicine.
In order to develop a graphene-based spintronic device, the challenge was to 'magnetise' the material, and researchers from Madrid have found the way through the quantum and nanoscience world.
The technique involves growing an ultra perfect grapheme film over a ruthenium single crystal inside an ultra high vacuum chamber whereorganic molecules of tetracyano-p-quinodimethane (TCNQ) are evaporated on the grapheme surface. TCNQ is a molecule that acts as a semiconductor at very low temperatures in certain compounds.
On observing results through an scanning tunnelling microscope (STM), scientists were surprised: organic molecules had organised themselves and were regularly distributed all over the surface, interacting electronically with the graphene-ruthenium substrate.
"We have proved in experiments how the structure of the TCNQ molecules over graphene acquireslong-range magnetic order, with electrons positioned in different bands according to their spin," clarifies Prof. Amadeo L. Vázquez de Parga.
Meanwhile, his colleague Prof. Fernando Martin has conducted modelling studies that have shown that, although graphene does not interact directly with the TCNQ, it does permit a highly efficient charge transfer between the substrate and the TCNQ molecules and allows the molecules to develop long range magnetic order.
The result is a new graphene-based magnetised layer, which paves the way towards the creation of devices based on what was already considered as the material of the future, but which now may also have magnetic properties.
####
About Plataforma SINC
The Scientific Information and News Service (Servicio de Información y Noticias Científicas - SINC), is a new public and nationwide multimedia scientific news platform supported by an open source software tool based in Spain. The primary objective behind the creation of SINC is to increase the number of high quality scientific news items in the media, as a means of bringing the public closer to science.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
SINC Team
Copyright © AlphaGalileo
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
Thin films
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Spintronics
![]() Quantum materials: Electron spin measured for the first time June 9th, 2023
Quantum materials: Electron spin measured for the first time June 9th, 2023
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








