Home > Press > Watching fluid flow at nanometer scales: Researchers find that tiny nanowires can lift liquids as effectively as tubes
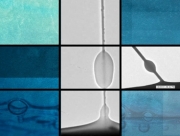 |
| Researchers find that tiny nanowires can lift liquids as effectively as tubes. |
Abstract:
Imagine if you could drink a glass of water just by inserting a solid wire into it and sucking on it as though it were a soda straw. It turns out that if you were tiny enough, that method would work just fine and wouldn't even require the suction to start.
Watching fluid flow at nanometer scales: Researchers find that tiny nanowires can lift liquids as effectively as tubes
Cambridge, MA | Posted on April 1st, 2013New research carried out at MIT and elsewhere has demonstrated for the first time that when inserted into a pool of liquid, nanowires wires that are only hundreds of nanometers (billionths of a meter) across naturally draw the liquid upward in a thin film that coats the surface of the wire. The finding could have applications in microfluidic devices, biomedical research and inkjet printers.
The phenomenon had been predicted by theorists, but never observed because the process is too small to be seen by optical microscopes; electron microscopes need to operate in a vacuum, which would cause most liquids to evaporate almost instantly. To overcome this, the MIT team used an ionic liquid called DMPI-TFSI, which remains stable even in a powerful vacuum. Though the observations used this specific liquid, the results are believed to apply to most liquids, including water.
The results are published in the journal Nature Nanotechnology by a team of researchers led by Ju Li, an MIT professor of nuclear science and engineering and materials science and engineering, along with researchers at Sandia National Laboratories in New Mexico, the University of Pennsylvania, the University of Pittsburgh, and Zhejiang University in China.
While Li says this research intended to explore the basic science of liquid-solid interactions, it could lead to applications in inkjet printing, or for making a lab on a chip. "We're really looking at fluid flow at an unprecedented small length scale," Li says so unexpected new phenomena could emerge as the research continues.
At molecular scale, Li says, "the liquid tries to cover the solid surface, and it gets sucked up by capillary action." At the smallest scales, when the liquid forms a film less than 10 nanometers thick, it moves as a smooth layer (called a "precursor film"); as the film gets thicker, an instability (called a Rayleigh instability) sets in, causing droplets to form, but the droplets remain connected via the precursor film. In some cases, these droplets continue to move up the nanowire, while in other cases the droplets appear stationary even as the liquid within them flows upward.
The difference between the smooth precursor film and the beads, Li says, is that in the thinner film, each molecule of liquid is close enough to directly interact, through quantum-mechanical effects, with the molecules of the solid buried beneath it; this force suppresses the Rayleigh instability that would otherwise cause beading. But with or without beading, the upward flow of the liquid, defying the pull of gravity, is a continuous process that could be harnessed for small-scale liquid transport.
Although this upward pull is always present with wires at this tiny scale, the effect can be further enhanced in various ways: Adding an electric voltage on the wire increases the force, as does a slight change in the profile of the wire so that it tapers toward one end. The researchers used nanowires made of different materials silicon, zinc oxide and tin oxide, as well as two-dimensional graphene to demonstrate that this process applies to many different materials.
Nanowires are less than one-tenth the diameter of fluidic devices now used in biological and medical research, such as micropipettes, and one-thousandth the diameter of hypodermic needles. At these small scales, the researchers found, a solid nanowire is just as effective at holding and transferring liquids as a hollow tube. This smaller scale might pave the way for new kinds of microelectromechanical systems to carry out research on materials at a molecular level.
The methodology the researchers developed allows them to study the interactions between solids and liquid flow "at almost the smallest scale you could define a fluid volume, which is 5 to 10 nanometers across," Li says. The team now plans to examine the behavior of different liquids, using a "sandwich" of transparent solid membranes to enclose a liquid, such as water, for examination in a transmission electron microscope. This will allow "more systematic studies of solid-liquid interactions," Li says interactions that are relevant to corrosion, electrodeposition and the operation of batteries.
The research was supported by Sandia National Laboratories, the U.S. Department of Energy, and the National Science Foundation.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Sarah McDonnell
617-253-8923
Copyright © Massachusetts Institute of Technology
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Nanoelectronics
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
![]() Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jόlich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jόlich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
![]() Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








