Home > Press > Engineers show feasibility of superfast materials: 'Organic topological insulators' for quantum computing
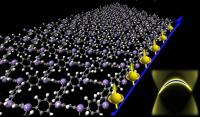 |
| University of Utah engineers demonstrated it is feasible to build the first organic materials that conduct electricity on their molecular edges, but act as an insulator inside. Called organic topological insulators, these materials are made from a thin molecular sheet (left) that resembles chicken wire and conducts electricity on its right edge (blue line) -- with the electrons carrying more information in the form of "up" spin. These new materials could be used to shuttle information at the speed of light in quantum computers due to the unique physical behavior a special class of electrons called Dirac fermions, depicted (right) in a plot of their energy and momentum.
Credit: Zhengfei Wang and Feng Liu, University of Utah |
Abstract:
University of Utah engineers demonstrated it is feasible to build the first organic materials that conduct electricity on their edges, but act as an insulator inside. These materials, called organic topological insulators, could shuttle information at the speed of light in quantum computers and other high-speed electronic devices.
Engineers show feasibility of superfast materials: 'Organic topological insulators' for quantum computing
Salt Lake City, UT | Posted on February 14th, 2013The study published this week in the journal Nature Communications will help pioneer a new field of research in materials science, in the same way organic materials lowered the cost and eased production of light-emitting diodes and solar cells, says senior author Feng Liu, professor and chair of materials science and engineering.
"This is the first demonstration of the existence of topological insulators based on organic materials," says Liu. "Our findings will broaden the scope and impact of these materials in various applications from spintronics to quantum computing."
While other researchers still must synthesize the new organic topological insulators, Liu says his team's previous work "shows we can engineer an interface between two different thin films to create topological insulators," in which electrons known as Dirac fermions move along the interface between two films, Liu adds.
Liu and his co-workers at the University of Utah's College of Engineering performed theoretical calculations to predict the existence of an organic topological insulator using molecules with carbon-carbon bonds and carbon-metal bonds, called an organometallic compound. For this new study, the team investigated how Dirac fermions move along the edges of this compound, which looks like a sheet of chicken wire.
To generate a topological insulator, scientists have to design materials that can transmit fermions. In a topological insulator, fermions behave like a massless or weightless packet of light, conducting electricity as they move very fast along a material's surface or edges. When these fermions venture inside the material, however, this "weightless" conductivity screeches to a halt.
What's more, Dirac fermions have a property called spin, or angular momentum around the particle's axis that behaves like a magnetic pole. This property gives scientists another way to place information into a particle because the spin can be switched "up" or "down." Such a mechanism could be useful for spin-based electronic devices, called spintronics, which can store information both in the charge and the spin of electrons.
"We have demonstrated a system with a special type of electron - a Dirac fermion - in which the spin motion can be manipulated to transmit information," Liu says. "This is advantageous over traditional electronics because it's faster and you don't have to worry about heat dissipation."
Earlier this year, Liu and his team discovered a "reversible" topological insulator in a system of bismuth-based compounds in which the behavior of ordinary or Dirac fermions could be controlled at the interface between two thin films. Bismuth is a metal best known as an ingredient of Pepto-Bismol. These theoretical predictions were confirmed experimentally by co-authors from Shanghai Jiaotong University in China.
Although inorganic topological insulators based on different materials have been studied for the last decade, organic or molecular topological insulators have not.
Liu conducted the study with Zhengfei Wang and Zheng Liu, both postdoctoral fellows in materials science and engineering at the University of Utah. The study was funded primarily by the U.S. Department of Energy, with additional support from the Army Research Laboratory and from the National Science Foundation through the University of Utah's Materials Research Science and Engineering Center.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Aditi Risbud
801-587-9038
University of Utah College of Engineering
72 S. Central Campus Dr., Room 1650 WEB
Salt Lake City, UT 84112
801-581-6911
fax: 801-581-8692
www.coe.utah.edu
Copyright © University of Utah
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Spintronics
![]() Quantum materials: Electron spin measured for the first time June 9th, 2023
Quantum materials: Electron spin measured for the first time June 9th, 2023
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Quantum Computing
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








