Home > Press > Deuterium Uptake in Magnetic Fusion Devices with Lithium Conditioned Carbon Walls: JICS-led collaborative research on lithium coatings unlocks mystery surrounding the harnessing of fusion energy
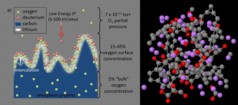 |
| Dynamic in lithiated graphite: a) Experiments show that deuterium bombardment dramatically increases the surface oxygen; b) Simulation shell for the D-impact chemistry in lithiated and oxidized carbon |
Abstract:
he research of a multi-institutional team from the U.S., Japan, and France, led by Predrag S. Krstic of the Joint Institute for Computational Sciences and Jean Paul Allain of Purdue University has answered the question of how the behavior of plasma—the extremely hot gases of nuclear fusion—can be controlled with ultra-thin lithium films on graphite walls lining thermonuclear magnetic fusion devices.
Deuterium Uptake in Magnetic Fusion Devices with Lithium Conditioned Carbon Walls: JICS-led collaborative research on lithium coatings unlocks mystery surrounding the harnessing of fusion energy
Knoxville, TN | Posted on February 1st, 2013 "It is remarkable that seemingly insignificant lithium depositions can profoundly influence the behavior of something as powerful as fusion plasmas," Krstic said.
Krstic and his team explain their research in a paper titled "Deuterium Uptake in Magnetic Fusion Devices with Lithium Conditioned Carbon Walls," recently accepted for publication in Physical Review Letters.
"How lithium coatings on graphite surfaces control plasma behavior has largely remained a mystery until our team was able to combine predictions from quantum-mechanical supercomputer simulations on the Kraken and Jaguar systems at Oak Ridge National Laboratory and in situ experimental results from the Purdue group to explain the causes of the delicate tunability of plasma behavior by a complex lithiated graphitic system," Krstic said. "Surprisingly, we find that the presence of oxygen in the surface plays the key role in the bonding of deuterium, while lithium's main role is to bring the oxygen to the surface. Deuterium atoms preferentially bind with oxygen and carbon-oxygen when there is a comparable amount of oxygen to lithium at the surface. That finding well matches a number of controversial experimental results obtained within the last decade."
The performance demands on plasma-facing components and the other materials that would surround future fusion power reactors is one of the reasons the U.S. National Academy of Engineering has ranked the quest for fusion as one of the top grand challenges for engineering in the 21st Century. Harnessing energy from thermonuclear magnetic fusion has been challenged in part by the extreme environment of hot and dense plasma interacting with the boundary fusion reactor walls. The strong coupling between the plasma edge and the wall surface, which causes erosion of the wall material, retention of radioactive tritium, and pollution of the plasma, has been hampered by a lack of fundamental understanding of what takes place at the interface where the plasma and solid material meet.
Recent research in which lithium coatings have been deposited on a variety of metallic and graphitic surfaces has provided evidence that plasma strongly responds on the deposited films. In fact, the use of ultra-thin coatings of lithium on graphite has resulted in an unprecedented influence on plasma behavior, including control of hydrogen recycling—one of the most important issues in the construction of future magnetic fusion-energy devices—and extraordinary improvements in energy confinement.
The study of the lithium coatings also impacts many areas beyond magnetic fusion, including nanoelectronics, lithium batteries, computational materials science, bioengineering and biophysics, plasma physics, and theoretical physics and chemistry.
"This work can lead to improvement of the hydrogen-recycling properties of the fusion materials facing plasma, as well as advancements in other areas," Krstic said. "We hope that our finding will inspire future theoretical and experimental work in diverse applications not only with lithium coatings on various materials but also with combinations of other types of materials that are potentially good ‘oxygen-getters'—for example elements of the first two groups of the periodic system."
Authors of the paper are P.S. Krstic, J.P. Allain, C.N. Taylor, J. Dadras, S. Maeda, K. Morokuma, J. Jakowski, A. Allouche, and C.H. Skinner. Support for the project was provided by the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE); the National Science Foundation (NSF), including its Extreme Science and Engineering Discovery Environment; and the Japan Science and Technology Agency.
Computational resources for the simulations were provided by the National Institute for Computational Sciences on the Kraken supercomputer, and the National Center for Computational Sciences on the Jaguar supercomputer. Laboratory experiments were conducted at Purdue University and Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory.
####
About Joint Institute for Computational Sciences
The Joint Institute for Computational Sciences was established by the University of Tennessee and Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL) to advance scientific discovery and state-of-the-art engineering, and to further knowledge of computational modeling and simulation. JICS pursues its mission by taking full advantage of petascale-and-beyond computers housed at ORNL, and by educating a new generation of scientists and engineers well-versed in the application of computational modeling and simulation for solving the most challenging scientific and engineering problems.
About NICS
The National Institute for Computational Sciences (NICS) operates the University of Tennessee supercomputing center, funded in part by the National Science Foundation. NICS is a major partner in NSF’s Extreme Science and Engineering Discovery Environment, known as XSEDE. The Remote Data Analysis and Visualization Center (RDAV) is a part of NICS.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Predrag Krstic
National Institute for Computational Sciences
Copyright © Joint Institute for Computational Sciences
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
Chemistry
![]() Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Thin films
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Nanoelectronics
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
![]() Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
![]() Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Alliances/Trade associations/Partnerships/Distributorships
![]() Chicago Quantum Exchange welcomes six new partners highlighting quantum technology solutions, from Chicago and beyond September 23rd, 2022
Chicago Quantum Exchange welcomes six new partners highlighting quantum technology solutions, from Chicago and beyond September 23rd, 2022
![]() University of Illinois Chicago joins Brookhaven Lab's Quantum Center June 10th, 2022
University of Illinois Chicago joins Brookhaven Lab's Quantum Center June 10th, 2022
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








