Home > Press > Exotic particles, chilled and trapped, form giant matter wave: Excitons form Bose-Einstein condensate
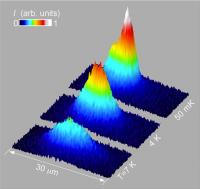 |
| As excitons cool to a fraction of a degree above absolute zero, they condense at the bottom of an electrostatic trap and spontaneously form coherent matter waves. Creating indirect excitons, with electrons and holes in separate layers of a semiconductor, allowed them to persist long enough to cool into this state.
Credit: Butov group/UCSD |
Abstract:
Physicists have trapped and cooled exotic particles called excitons so effectively that they condensed and cohered to form a giant matter wave.
Exotic particles, chilled and trapped, form giant matter wave: Excitons form Bose-Einstein condensate
San Diego, CA | Posted on May 24th, 2012This feat will allow scientists to better study the physical properties of excitons, which exist only fleetingly yet offer promising applications as diverse as efficient harvesting of solar energy and ultrafast computing.
"The realization of the exciton condensate in a trap opens the opportunity to study this interesting state. Traps allow control of the condensate, providing a new way to study fundamental properties of light and matter," said Leonid Butov, professor of physics at the University of California, San Diego. A paper reporting his team's success was recently published in the scientific journal Nano Letters.
Excitons are composite particles made up of an electron and a "hole" left by a missing electron in a semiconductor. Created by light, these coupled pairs exist in nature. The formation and dynamics of excitons play a critical role in photosynthesis, for example.
Like other matter, excitons have a dual nature of both particle and wave, in a quantum mechanical view. The waves are usually unsynchronized, but when particles are cooled enough to condense, their waves synchronize and combine to form a giant matter wave, a state that others have observed for atoms.
Scientists can easily create excitons by shining light on a semiconductor, but in order for the excitons to condense they must be chilled before they recombine.
The key to the team's success was to separate the electrons far enough from their holes so that excitons could last long enough for the scientists to cool them into a condensate. They accomplished this by creating structures called "coupled quantum wells" that separate electrons from holes in different layers of alloys made of gallium, arsenic and aluminum.
Then they set an electrostatic trap made by a diamond-shaped electrode and chilled their special semiconducting material in an optical dilution refrigerator to as cold as 50 milli-Kelvin, just a fraction of a degree above absolute zero.
A laser focused on the surface of the material created excitons, which began to accumulate at the bottom of the trap as they cooled. Below 1 Kelvin, the entire cloud of excitons cohered to form a single matter wave, a signature of a state called a Bose-Einstein condensate.
Other scientists have seen whole atoms do this when confined in a trap and cooled, but this is the first time that scientists have seen subatomic particles form coherent matter waves in a trap.
Varying the size and depth of the trap will alter the coherent exciton state, providing this team, and others, the opportunity to study the properties of light and mater in a new way.
This most recent discovery stems from an ongoing collaboration between Leonid Butov's research group in UC San Diego's Division of Physical Sciences, including Alexander High, Jason Leonard and Mikas Remeika, and Micah Hanson and Arthur Gossard in UC Santa Barbara's Materials Department. The Army Research Office and the National Science Foundation funded the experiments, and the Department of Energy supported the development of spectroscopy in the optical dilution refrigerator, the technique used to observe the exciton condensate in a trap.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Susan Brown
858-246-0161
Copyright © University of California - San Diego
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Quantum Computing
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
![]() Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








