Home > Press > Rensselaer Engineers “Cook” Promising New Heat-Harvesting Nanomaterials in Microwave Oven: Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute Researchers Create Large Marble-Sized Pellets of Thermoelectric Nanomaterials
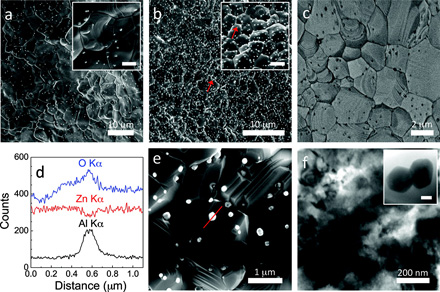 |
| Engineering researchers at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute have developed new thermoelectric nanomaterials, pictured above, that could lead to techniques for better capturing and putting this waste heat to work. The key ingredients for making marble-sized pellets of the new material are aluminum and a common, everyday microwave oven. |
Abstract:
Waste heat is a byproduct of nearly all electrical devices and industrial processes, from driving a car to flying an aircraft or operating a power plant. Engineering researchers at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute have developed new nanomaterials that could lead to techniques for better capturing and putting this waste heat to work. The key ingredients for making marble-sized pellets of the new material are aluminum and a common, everyday microwave oven.
Rensselaer Engineers “Cook” Promising New Heat-Harvesting Nanomaterials in Microwave Oven: Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute Researchers Create Large Marble-Sized Pellets of Thermoelectric Nanomaterials
Troy, NY | Posted on September 29th, 2011Harvesting electricity from waste heat requires a material that is good at conducting electricity but poor at conducting heat. One of the most promising candidates for this job is zinc oxide, a nontoxic, inexpensive material with a high melting point. While nanoengineering techniques exist for boosting the electrical conductivity of zinc oxide, the material's high thermal conductivity is a roadblock to its effectiveness in collecting and converting waste heat. Because thermal and electrical conductivity are related properties, it's very difficult to decrease one without also diminishing the other.
However, a team of researchers led by Ganpati Ramanath, professor in the Materials Science and Engineering Department at Rensselaer, in collaboration with the University of Wollongong, Australia, have demonstrated a new way to decrease zinc oxide's thermal conductivity without reducing its electrical conductivity. The innovation involves adding minute amounts of aluminum to zinc oxide, and processing the materials in a microwave oven. The process is adapted from a technique invented at Rensselaer by Ramanath, graduate student Rutvik Mehta, and Theo Borca-Tasciuc, associate professor in the Department of Mechanical, Aerospace, and Nuclear Engineering (MANE). This work could open the door to new technologies for harvesting waste heat and creating highly energy efficient cars, aircraft, power plants, and other systems.
"Harvesting waste heat is a very attractive proposition, since we can convert the heat into electricity and use it to power devices — like in a car or a jet — that is creating the heat in the first place. This would lead to greater efficiency in nearly everything we do and, ultimately, reduce our dependence on fossil fuels," Ramanath said. "We are the first to demonstrate such favorable thermoelectric properties in bulk-sized high-temperature materials, and we feel that our discovery will pave the way to new power harvesting devices from waste heat."
Results of the study are detailed in the paper "Al-Doped Zinc Oxide Nanocomposites with Enhanced Thermoelectric Properties," published recently by the journal Nano Letters. View the paper online at: http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/nl202439h
To create the new nanomaterial, researchers added minute quantities of aluminum to shape-controlled zinc oxide nanocrystals, and heated them in a $40 microwave oven. Ramanath's team is able to produce several grams of the nanomaterial in a matter of few minutes, which is enough to make a device measuring a few centimeters long. The process is less expensive and more scalable than conventional methods and is environmentally friendly, Ramanath said. Unlike many nanomaterials that are fabricated directly onto a substrate or surface, this new microwave method can produce pellets of nanomaterials that can be applied to different surfaces. These attributes, together with low thermal conductivity and high electrical conductivity, are highly suitable for heat harvesting applications.
"Our discovery could be key to overcoming major fundamental challenges related to working with thermoelectric materials," said project collaborator Borca-Tasciuc. "Moreover, our process is amenable to scaling for large-scale production. It's really amazing that a few atoms of aluminum can conspire to give us thermoelectric properties we're interested in."
This work was a collaborative effort between Ramanath and Shi Xue Dou, a professor at the Institute for Superconducting and Electronic Materials at the University of Wollogong, Australia. Wollongong graduate student Priyanka Jood carried out the work together with Rensselaer graduate students Rutvik Mehta and Yanliang Zhang during Jood's one-year visit to Rensselaer. Co-authors of the paper are Richard W. Siegel, the Robert W. Hunt Professor of Materials Science and Engineering; along with professors Xiaolin Wang and Germanas Peleckis at the University of Wollongong.
This research is funded by support from IBM through the Rensselaer Nanotechnology Center; S3TEC, an Energy Frontier Research Center funded by the U.S. Department of Energy (DoE) Office of Basic Energy Sciences; the Australian Research Council (ARC); and the University of Wollongong.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Michael Mullaney
Phone: (518) 276-6161
Copyright © Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute (RPI)
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() “Nanosculpture” Could Enable New Types of Heat Pumps and Energy Converters:
“Nanosculpture” Could Enable New Types of Heat Pumps and Energy Converters:
![]() Inexpensive “Nanoglue” Can Bond Nearly Anything Together:
Inexpensive “Nanoglue” Can Bond Nearly Anything Together:
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








