Home > Press > Nanoscale spin waves can replace microwaves
 |
Abstract:
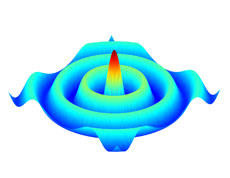
A group of scientists from the University of Gothenburg and the Royal Institute of Technology (KTH), Sweden, have become the first group in the world to demonstrate that theories about nanoscale spin waves agree with observations. This opens the way to replacing microwave technology in many applications, such as mobile phones and wireless networks, by components that are much smaller, cheaper, and that require less resources. The study has been published in the scientific journal Nature Nanotechnology, the most prestigious journal in nanoscience.
Nanoscale spin waves can replace microwaves
Gothenburg, Sweden | Posted on September 8th, 2011"We have been in competition with two other research groups to be the first to confirm experimentally theoretical predictions that were first made nearly 10 years ago. We have been successful due to our method for constructing magnetic nanocontacts and due to the special microscope at our collaborators' laboratory at the University of Perugia in Italy", says Professor Johan Åkerman of the Department of Physics, University of Gothenburg, where he is head of the Applied Spintronics group.
The aim of the research project, which started two years ago, has been to demonstrate the propagation of spin waves from magnetic nanocontacts. Last autumn, the group was able to demonstrate the existence of spin waves with the aid of electrical measurements, and the results were published in the scientific journal Physical Review Letters. The new results have been published in Nature Nanotechnology, the most prestigious journal in nanoscience.
The research group has used one of the three advanced spin wave microscopes in the world, at the university in the Italian town of Perugia, to visualise the motion. The microscope makes it possible to see the dynamic properties of components with a resolution of approximately 250 nanometre.
The results have opened the way for a new field of research known as "magnonics", using nanoscale magnetic waves.
"I believe that our results will signal the start of a rapid development of magnonic components and circuits. What is particularly exciting is that these components are powered by simple direct current, which is then converted into spin waves in the microwave region. The frequency of these waves can be directly controlled by the current. This will make completely new functions possible", says Johan Åkerman, who is looking forward to exciting developments in the next few years.
Its magneto-optical and metallic properties mean that magnonic technology can be integrated with traditional microwave-based electronic circuits, and this will make completely untried combinations of the technologies possible. Magnonic components are much more suitable for miniaturisation than traditional microwave technology.
Full bibliographic information
Jorunal: Nature Nanotechnology Year published:(2011) doi:10.1038/nnano.2011.140
Title: Direct observation of a propagating spin wave induced by spin-transfer torque
Authors: M. Madami, S. Bonetti, G. Consolo, S. Tacchi, G. Carlotti, G. Gubbiotti, F. B. Mancoff, M. A. Yar & J. Åkerman
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Johan Åkerman
Department of Physics
University of Gothenburg
+46 (0)31 786 9147
Copyright © AlphaGalileo
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Spintronics
![]() Quantum materials: Electron spin measured for the first time June 9th, 2023
Quantum materials: Electron spin measured for the first time June 9th, 2023
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








